
Editor’s Note: Social media data mining has evolved significantly since we first published this guide. This 2026 edition includes the latest updates to social media data mining tools, techniques, AI/ML integration in social data mining, updated privacy compliance requirements, and the latest trends and insights.
Editor’s Note: Social media data mining has evolved significantly since we first published this guide. This 2026 edition includes the latest updates to social media data mining tools, techniques, AI/ML integration in social data mining, updated privacy compliance requirements, and the latest trends and insights.
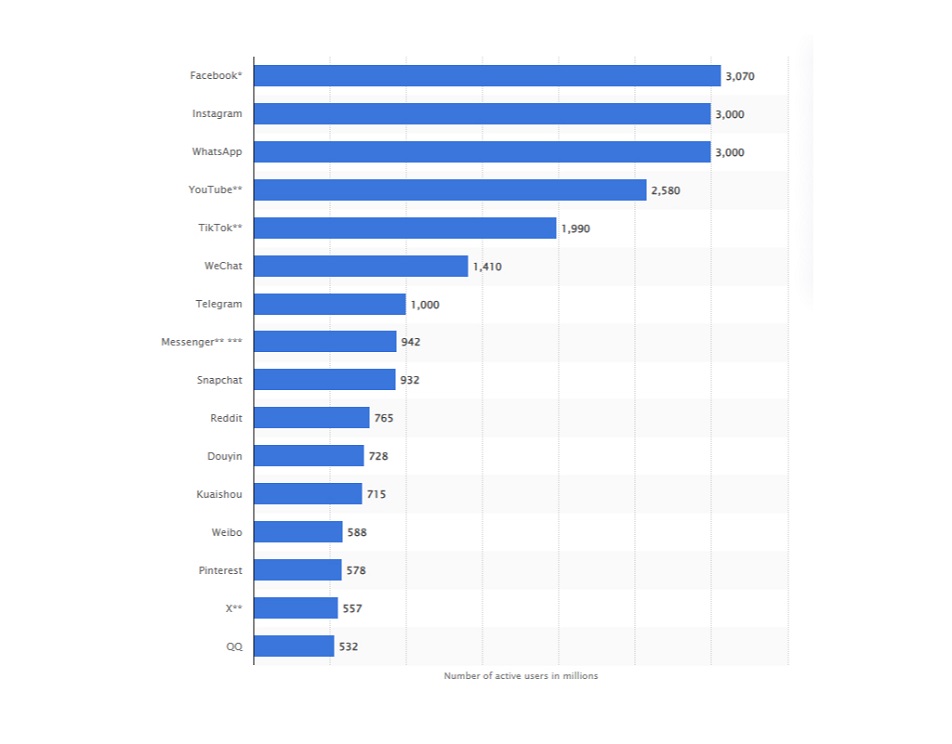
The present-day digital ecosystem is powered by a relentless engine: over 5.6 billion individuals actively engaging across global social media platforms. Every single post, comment, and network connection contributes to an unparalleled, live repository of human behavior and market dynamics. For businesses, this unprecedented volume of unstructured data is not a peripheral concern; it is the defining frontier of competitive intelligence.
But the true challenge is strategic social data extraction and precise interpretation. Social media data mining is the authoritative, rigorous discipline for tackling this challenge. It helps analyze user behavior, measure sentiment, and map social networks. It transforms vast, noisy user-generated data streams into clear, actionable competitor and target market intelligence, revealing critical patterns invisible to surface-level analysis.
What Is Social Media Data Mining?
Social media data mining, also known as social media mining, is the process of collecting, processing, and analyzing the vast amounts of raw data generated on social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter (now X), LinkedIn, and TikTok.
Data mining for social media involves using various techniques and tools to discover and analyze patterns, sentiments, hidden trends, user behavior, and relevant information from user-generated content. The content may be posts, comments, and interactions.
Social Media Data Mining Techniques
The primary goal of social media mining is to inform decision-making across marketing, customer engagement, competitive intelligence, and related functions (e.g., understanding audience demographics or monitoring brand perception).
Here are some techniques that can be used to get insights from social media:
1. Sentiment Analysis
- Highly effective for understanding the emotional tone behind social media content (positive, negative, neutral).
- Helps in gauging public opinion on brands, products, or services
- Used to monitor brand reputation and detect emerging customer concerns.
2. Social Network Analysis (SNA) / Graph Mining
- Crucial for understanding relationships, user interactions, and community structures within social networks.
- Helpful in identifying key influencers, detecting communities, and understanding how information spreads across the network.
3. Clustering
- Effective for grouping users or posts with similar behaviors, interests, or characteristics.
- Used to segment customers for targeted marketing, personalize content recommendations, and identify niche communities.
4. Predictive Analytics
- Essential for forecasting future trends, user engagement, and behavior based on historical data.
- Helps in forecasting the success of campaigns, predicting customer churn, or anticipating trends in social media discussions.
5. Topic Modeling
- Powerful for discovering hidden topics or themes within large volumes of text data.
- Used for uncovering emerging trends and key discussions happening on social media that help in content creation and engagement strategies.
Social Media Data Mining: Why Do It & How It Helps?
Using data from the web in innovative ways can make a significant difference. The way social media data is harvested and used is a crucial factor that sets a flourishing business apart from a failing one. This is because social media data mining plays a pivotal role in all aspects of business operations—from the conception of a product to its maturity. It has a significant role in marketing, casting light on the four Ps: Product, Price, Promotion, and Place. Without the quality and quantity of data that social media mining can provide, companies may struggle to connect with the audience intimately, leading to ineffective marketing campaigns.
The primary goal of social data mining is to gain a deeper understanding of user behavior, preferences, values, interests, and opinions, and to uncover hidden trends and patterns. These insights are used to make informed decisions in introducing new products, designing marketing strategies, or improving existing processes or services.
In fact, research by Deloitte Digital shows that companies that place social media and community at the core of their strategy achieved an average revenue growth of 10.2% in 2022, and in their B2C business lines, they are eight times more likely to have surpassed revenue targets by 25% or more. The Deloitte Digital State of Social Research (2025) states that social media budgets grew by an average of 9% from 2023 to 2024.

How Can Social Media Data Mining Help Businesses?
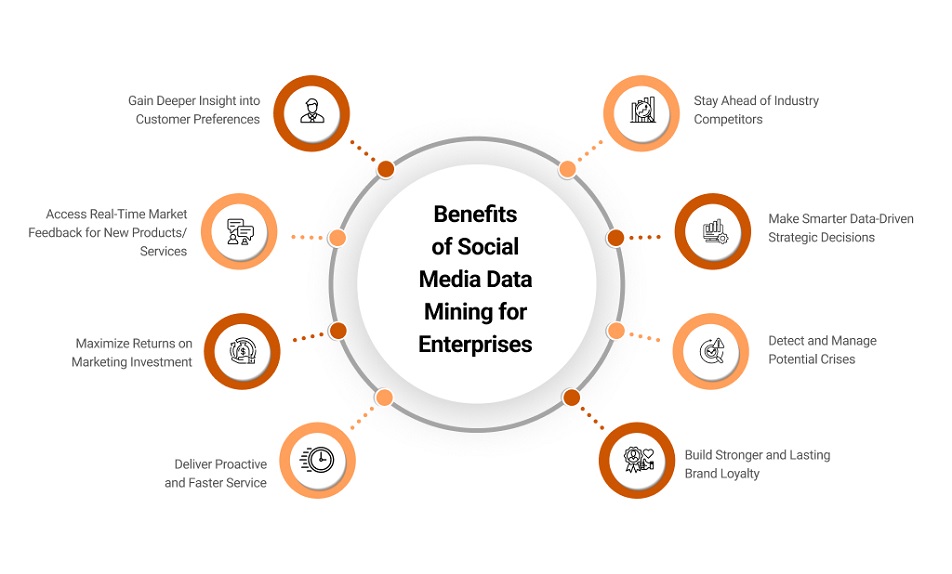
Ignoring social network mining can be costly. Businesses risk losing touch with customers and failing to adapt to the market dynamics. This may result in failing to address customer needs promptly or adequately, missing opportunities, and ceding competitive advantage to rivals.
On the flipside, there are several benefits of mining social data and driving business strategies using it:
1. Better Competitive Intelligence
Social media mining is a powerful tool for competitive intelligence. It allows businesses to
- Monitor brand mentions of competitors to determine their market perception
- Filter for “negative” mentions of a competitor to understand the target market opinion
- Compare the mentions of their brand vs. their competitors to identify engagement/reach differences
- Analysing their pricing strategy or product positioning
- Analyzing which of their topics, keywords, and media formats gain more reach
By tracking competitors’ performance, you can benchmark their efforts and identify opportunities for improvement. Mining social media data can also help uncover areas competitors may be overlooking, allowing you to capitalize on those gaps. Overall, it helps companies stay ahead of the competition and innovate more effectively.
2. Honing Brand Perception
Through social media data mining, businesses can gauge public perception of their brand image and proactively engage with customers to foster a positive brand image.
By segmenting users into advocates and detractors, enterprises can move beyond passive listening to active reputation management. This data enables brands to encourage their supporters to engage in organic advocacy (to spread positive word-of-mouth) while simultaneously deploying targeted interventions to resolve grievances for unhappy customers, effectively neutralizing PR risks before they escalate.
3. Understanding Customers Better

Social media platforms contain valuable customer profile details, such as age, gender, behavior, location, education, occupation, interests, engagement patterns, social connections, and online activity, which can help companies develop customer-centric business strategies.
For example, with LinkedIn data mining, a business can analyze users’ professional backgrounds, such as their job titles, work experience, and industry connections, to identify potential clients, partners, or talent.
Social data mining also enables close monitoring of customer attitudes and feedback. And, it provides direct insights into customer satisfaction. This understanding is crucial for creating personalized engagement, improving customer experience, and curating engaging content.
4. Identifying Emerging Trends
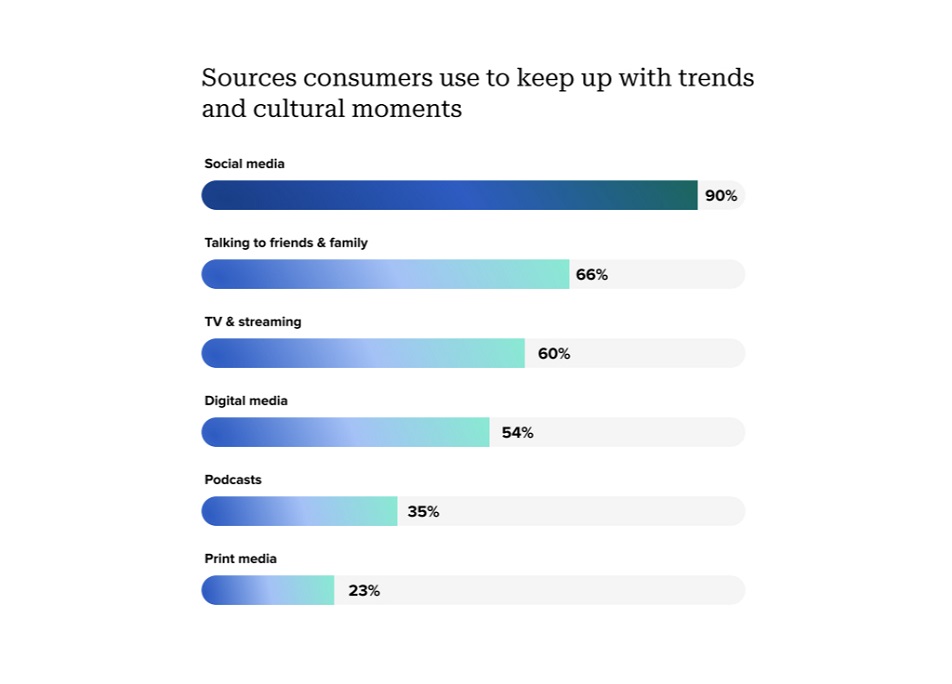
Social media is where trends either originate or gain momentum. According to the 2025 Sprout Social Index, about 90% of consumers use social media to stay up to date on cultural events and trends. However, the volume of data generated on social media platforms and the scale of activity make it difficult to identify patterns, let alone spot trends.
With a suitable social media data mining technique, identifying patterns and trends becomes easier. Analyzing the frequency and context of the topics gaining popularity provides insights into emerging discussions and interests. This facilitates assessing the users’ sentiment around certain topics and their overall mood and perception.
And, by analyzing historical social media data, companies can identify shifts in user behavior over time, compare past and present trends, and anticipate future developments. By proactively evaluating and anticipating emerging trends, companies can adapt their strategies, products, and services so that they align with evolving customer preferences and industry developments. For example, a surge in specific jargon or visual aesthetics on TikTok can alert a product team to a shifting consumer preference before a single competitor reacts.
5. Enhancing Marketing Campaign Effectiveness
By 2025, social media advertising spending is projected to reach $276.7 billion, reflecting how businesses are redesigning their marketing efforts.
As competition for consumer attention intensifies, it becomes crucial for companies to ensure their marketing budget is spent wisely. This is where social media data mining comes into play. By analyzing social media data, companies can gain deep insights into their target audience’s demographics, behaviors, preferences, and values. This level of detail allows businesses to segment their audience more precisely and tailor marketing efforts to be more relevant and personalized, ultimately optimizing their ad spend.
Furthermore, data mining also aids in identifying key influencers and thought leaders within specific industries who resonate with the brand’s target audience. Collaborating with these influencers can amplify marketing reach and increase brand awareness, making campaigns not only more targeted but also more effective in driving engagement and conversions.
6. Driving Product Innovation
Social data mining accelerates product innovation by providing real-time insights into customer preferences, pain points, and frustrations with existing products that users express naturally over social channels. It enables businesses to identify unmet needs, validate new concepts, and engage directly with users through polls and Q&As.
It also allows the development of customer-centric products tailored to specific market segments, resulting in faster adaptation and more successful product launches while minimizing market risk.
7. Improving Customer Retention
By analyzing the “digital footprints” of their existing user base, businesses can identify shifts in sentiment or engagement levels (e.g., public complaints or reduced brand mentions). Social media data mining enables proactive service (detecting dissatisfaction early and triggering win-back campaigns before customers leave), personalized marketing (using customer behavior data to design relevant content & promotions), and the identification of at-risk customers through churn prediction (enabling timely intervention to address concerns).
By using intent signals from social data to foster a stronger sense of community and deliver tailored experiences, businesses can build stronger, more loyal relationships, driving engagement and improving long-term retention.
Social Network Mining vs Social Media Mining
Social media data mining focuses on extracting meaning from user-generated content. Social network mining focuses on understanding the relationships and interactions among users.
Together, they offer a more comprehensive approach to analyzing online behavior.
By understanding how people are connected (social network mining) versus what they are saying (social media mining), organizations can unlock more precise insights, tailor their engagement efforts, and ultimately drive better outcomes.
While both techniques draw data from social media platforms, knowing the distinction between social media mining and social network mining is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their strategies using social media data.
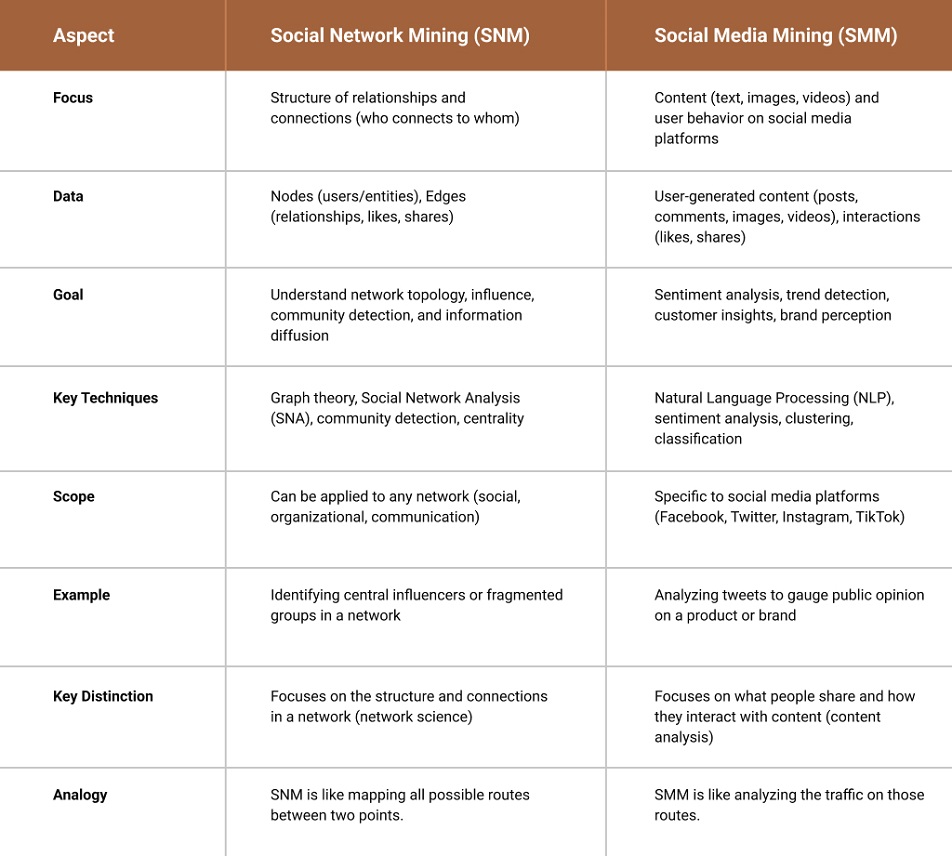
Together, social network mining and social media mining provide a full-spectrum analysis of both the structural framework and the content flowing through social media networks. Understanding both the ‘who’ and the ‘what’ of social interactions allows businesses to craft more effective, targeted strategies.
Social Media Data Mining Process
The process of data mining for social media involves a number of key aspects, and it can seem daunting. The volume, variety, and velocity of the content generated on social media platforms are huge, and any large-scale mining effort is challenging. But with the right tools and systematic execution, it is possible to effectively mine social media data in all its abundance.
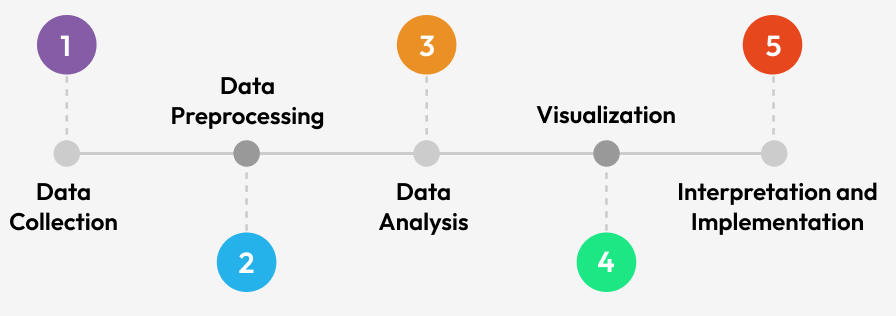
The following are the key steps involved in the social media data mining process.
1. Data Collection
The initial phase of the social media data mining process is the collection of raw data systematically from various platforms. This involves selecting the specific platforms and gathering the data using methods like APIs and web scraping to access relevant data. Since the density of information is a challenge, depending on the end goal, the scope of the social media data collection can be narrowed by applying filters based on keywords, hashtags, topics, users, location, or time.
This stage lays the groundwork for subsequent steps of the social media data mining process. It provides the raw material for analysis, interpretation, and extraction of actionable insights. So, it is important to carefully select the method for data collection, focusing on the sources and types of data relevant to analysis.
2. Data Preprocessing
No matter the methods and tools used for collecting social media data, there will be duplicates, inaccuracies, and incompleteness in the data. This is true even for AI-powered social media data mining tools – AI hallucination rates still vary largely (15-35% as found in independent studies) depending on the model and domain (higher in legal/medical).
This requires refining the collected data — cleaning the data, filtering, transforming, and enriching to remove noise, duplicates, and errors, ensuring overall consistency in the dataset. The objective is to transform the raw data into a well-organized and standardized format to facilitate accurate and reliable analysis. Preprocessing is a crucial step as it helps ensure the quality, validity, and reliability of the collected data.
3. Data Analysis
This phase involves analyzing the preprocessed data to find patterns, trends, and associations between data points and uncovering insights. This could include identifying common words or phrases or the frequency of their occurrence, periods of high engagement, prevalent sentiments across posts, and how these are distributed geographically or temporally. The results thus obtained serve as the foundation for informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Various analytical techniques may be employed to discover hidden trends and patterns. These include classification, clustering, association, regression, anomaly detection, and recommendation.
4. Data Visualization
The analyzed data and the results gathered do not fully give a clear picture. Visualization of the data is what gives better clarity and understanding. Data visualization helps bring key points and areas of prominence to the fore, revealing patterns and relationships that may otherwise remain hidden, and allows for better comparison of the differences. It makes the data more interpretable and easier to grasp.
Visualization is not (only) about making the data presentable; it’s about facilitating the discovery of patterns. So choosing suitable formats for data visualization is essential. Line graphs, for example, are suitable for visualizing temporal data, and linear regression graphs may be used to visualize correlations.
5. Data Interpretation and Implementation
This stage of the social media data mining process involves making sense of the data and drawing conclusions from the results. What do the patterns and relationships signify? Do they have any meaningful association? How do they compare with results from the past? These and other questions need to be answered.
Types of Data Collected via Social Media Mining
Social media mining involves collecting diverse data to understand audience behavior, market trends, and brand perception. The key types of data collected include:
User/Profile Data
|
Content Data
|
Engagement & Interaction Data
|
Behavioral & Sentiment Data
|
This wide array of data provides businesses with comprehensive insights for marketing, product development, and customer engagement strategies.
Top 7 Social Media Data Mining Tools for Enterprises [for 2026]
Having the right social media data mining tools at your disposal can streamline data collection, enhance analysis, and uncover valuable insights with greater efficiency. They can help you go beyond tracking and scheduling posts through advanced features, like analytics, social listening, and sentiment analysis.
The following are the top social media data mining tools in 2026 that empower enterprises to leverage advanced capabilities for deeper insights, trend identification, and competitive advantage. This selection is based on a comparative analysis of enterprise-grade features, market share, and user feedback, ensuring each tool meets the rigorous security and scalability demands of large-scale enterprise operations.
1. Sprinklr
- Strength: Comprehensive AI-powered social media platform.
- Features: Advanced AI-driven insights, multi-channel integration, pre-built queries, competitive intelligence, and real-time reporting.
- Why It Matters: Ideal for large enterprises needing comprehensive data management across multiple social platforms, with custom reporting and analytics.
2. Brandwatch
- Strength: Deep social listening and audience intelligence.
- Features: Advanced sentiment analysis, influencer identification, topic clustering, and historical data tracking.
- Why It Matters: Helps enterprises track brand sentiment, customer behavior, and competitive intelligence to refine strategies and make data-driven decisions.
3. Sprout Social
- Strength: All-in-one social media management platform with data mining capabilities.
- Features: Social listening, sentiment analysis, detailed performance reports, and cross-channel management.
- Why It Matters: Sprout Social’s comprehensive suite is designed to help enterprises engage with audiences, analyze trends, and optimize marketing strategies.
4. Hootsuite
- Strength: Social media management and analytics.
- Features: Cross-platform publishing, competitive benchmarking, detailed analytics, and real-time engagement insights.
- Why It Matters: Hootsuite’s strong focus on multi-account management and in-depth analytics makes it an enterprise favorite for managing large social media operations.
5. Meltwater
- Strength: Integrates media monitoring with social data mining for deeper insights.
- Features: Media and social listening, real-time trend tracking, influencer insights, and access to historical data.
- Why It Matters: Ideal for enterprises requiring comprehensive media and social data for global strategy management and brand health monitoring.
6. Keyhole
- Strength: Real-time social media analytics with a focus on market research and influencers.
- Features: Hashtag tracking, influencer discovery, performance tracking, and trend spotting.
- Why It Matters: Keyhole is great for enterprises looking to analyze real-time social data, track influencer effectiveness, and measure hashtag performance.
7. Brand24
- Strength: AI-powered social listening and brand monitoring.
- Features: Brand mention tracking, sentiment analysis, online conversation monitoring, and alerts for negative mentions.
- Why It Matters: Helps businesses stay on top of brand sentiment, track mentions in real time, and address customer concerns before they escalate.
Challenges in Social Media Data Mining
The most concerning social media data mining challenges can be broadly categorized into data-related issues, technical hurdles, and ethical and legal concerns.

Data-Related Challenges
- High Volume, Velocity, and Variety (Big Data): The massive volume and speed of data generated in real-time, coupled with diverse data types, require scalable solutions for efficient storage and analysis.
- Data Quality and Noise: Social media data is often unstructured and filled with noise (e.g., spam, fake accounts, slang), making data cleaning and preprocessing essential to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Data Heterogeneity and Integration: Data is collected in various formats (text, images, videos, geolocation) from different platforms, making it challenging to integrate and process into a cohesive dataset for analysis.
- Data Representativeness and Bias: Social media users may not uniformly represent the general population, leading to biased datasets that can skew results and affect the accuracy of insights.
Technical and Operational Challenges
- Scalability and Real-Time Analysis: Real-time data processing requires scalable frameworks and advanced algorithms, which can be computationally demanding.
- Algorithm Complexity and Interpretability: Advanced machine learning models like Transformers and Recurrent Neural Networks used in social media data mining are often considered "black boxes", making it difficult to interpret and understand how decisions or insights are derived.
- Data Access Limitations: APIs and privacy restrictions on social media platforms (which limit how their data can be accessed) hinder large-scale data scraping and collection, potentially hindering in-depth analysis.
- Resource Demands: Effective data mining requires significant computational resources, specialized tools, and skilled personnel, which can be a barrier for smaller enterprises.
Ethical and Legal Challenges
- Privacy Concerns and Consent: Collecting personal user data raises privacy concerns; compliance with GDPR and CCPA is necessary, as well as obtaining informed consent from users for ethical data collection.
- Ethical Dilemmas and Bias: Mining social media data can reinforce biases or discriminate if algorithms are trained on biased datasets, making it crucial to address ethical concerns and ensure responsible use.
- Misinformation and Trust Issues: The spread of misinformation complicates the trustworthiness of social media data, requiring businesses to distinguish genuine insights from fake news or bot-driven content.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Storing large amounts of sensitive data exposes businesses to cybersecurity threats; robust data protection measures, like encryption, are critical to securing user information.
The "Automation Bias" Challenges
The current biggest challenge in social media data mining is over-reliance on AI-generated insights, assuming the algorithm is "correct" even when it lacks the nuance of human cultural context.
To maintain data integrity, businesses are now shifting toward a Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) framework, treating AI as a "Co-Pilot," not an "Auto-Pilot." By maintaining a human-in-the-loop, organizations ensure that their social intelligence is not just fast, but accurate, ethical, and culturally resonant.
Platform-Specific Social Media Data Mining Strategies for 2026
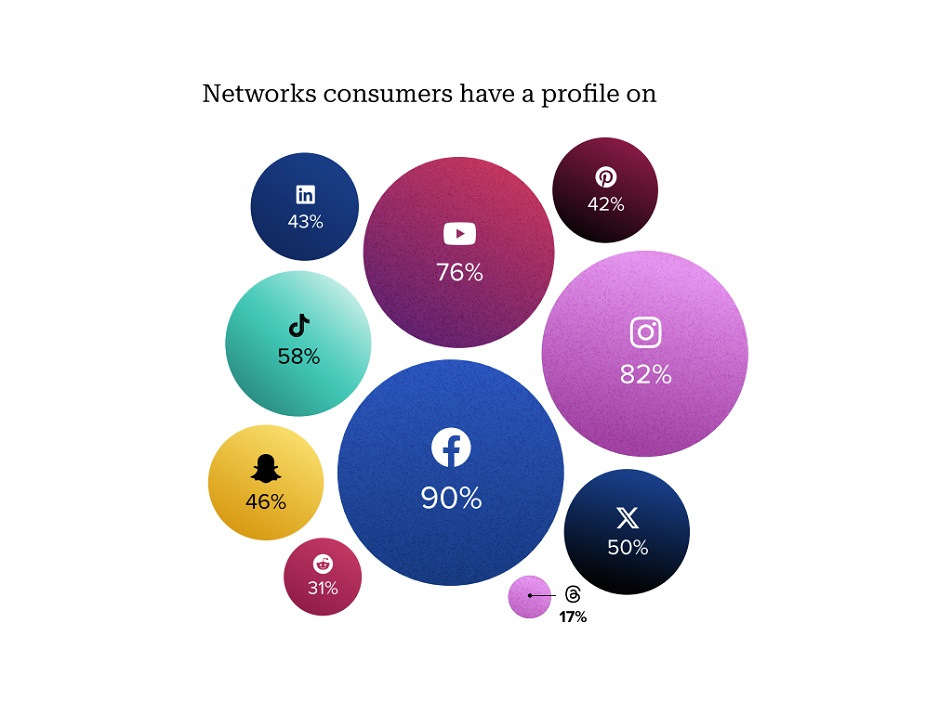
As social media platforms continue to evolve, businesses must adapt their data mining strategies to the unique characteristics of each platform. In 2026, platform-specific strategies will be key to maximizing engagement, refining targeting, and driving conversions:
- TikTok & Instagram Reels (Short-Form Video): Focus on watch time, shares, and comments to understand user interests and identify viral trends. Use AI-driven insights to optimize content and achieve micro-virality.
- Instagram & Facebook (Community & Commerce): Analyze direct messages, story interactions, and in-app shopping data to build engaged communities and drive conversions through seamless social commerce.
- LinkedIn (B2B & Professional Insights): Leverage network analysis and engagement within professional groups to identify decision-makers, industry trends, and thought leadership opportunities.
- X & Reddit (Real-Time Trends & Sentiment): Use sentiment analysis to track emerging trends, public opinion, and potential crises in real time, while identifying influencers and niche communities.
- Pinterest (Visual Discovery & Purchase Intent): Track pins, clicks, and search queries to understand visual discovery and user purchase intent, optimizing content and campaigns for higher engagement.
Where Is the Future of Social Media Data Mining Headed?
The global social media analytics market was estimated at $8.84 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a strong compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.43% from 2026 to 2032, reaching 46.49 billion in 2032. The continued growth in market size is a clear indication that the upcoming year will bring social media data mining to the core of business strategies.
But is it heading toward a direction where the data mining process becomes more specific, precise, and reliable without creating security risks? Let’s find out.
Here’s a look at where things are heading in 2026 and beyond for social media data mining:
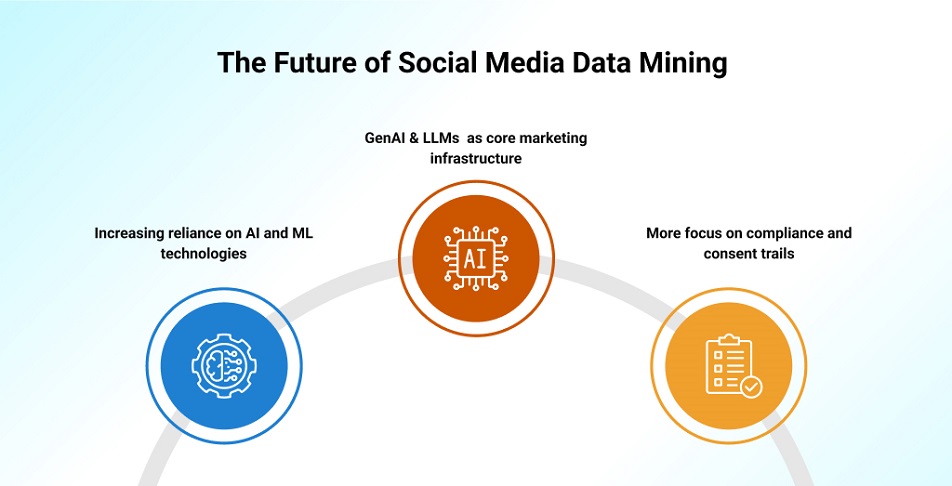
1. AI and Machine Learning Integrated Social Data Mining
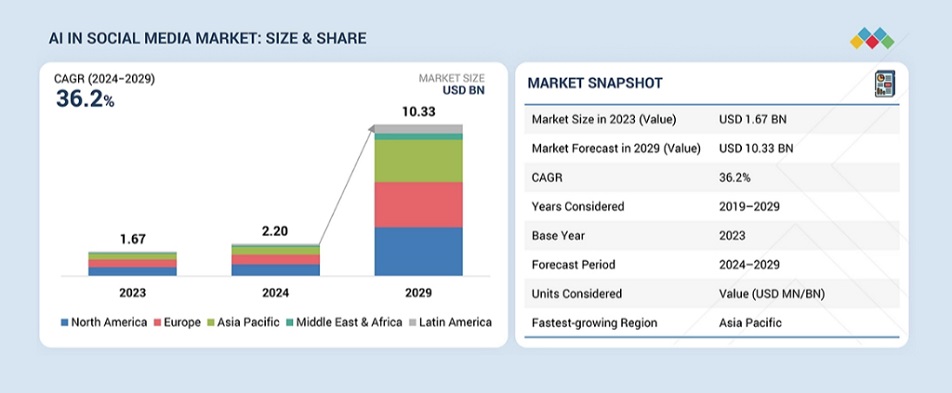
The global AI in social media market is expected to cross USD 10.33 billion in 2029, up from USD 2.20 billion in 2024, at a CAGR of 36.2%. The largest segment of this market isn't just data storage; it is Social Media Management (Social Listening & Engagement). Industries with the highest regulatory stakes and "need for precision" (Healthcare & Pharma) are the ones leaning hardest into AI mining (projected to grow at the highest rate of 42.3% CAGR).
This rapid growth highlights the increasing reliance on AI and ML technologies to harness the vast potential of social media data. Here’s what that looks like for businesses relying on social data mining:
- Better Strategic Agility: We are moving away from passive 'listening' to active 'intelligence-led execution,' where mining insights are instantly transformed into content strategy.
- Operational Autonomy with Real-time AI Agents: In 2026, AI agents are expected to automatically draft the response, identify the influencer, and suggest the content pivot in real-time, relevant to your target audience.
- Better Authenticity Safeguards against Synthetic Misinformation: With rising synthetic content and deepfakes, social media data mining will be expected to serve as a critical defense layer, verifying the authenticity of audience sentiment and protecting brands from AI-driven misinformation
- "Personalization at Scale" as the #1 Market Driver: AI integration allows enterprises to move from 'segmenting groups' to 'understanding individuals.’ In 2026, businesses will be expected to deliver hyper-targeted engagement that mirrors the precision of a 1-on-1 conversation.
2. Generative AI and LLMs for Mining Social Data
2026 marks the shift from 'pilot' to 'production.' We are moving from 'Can it work?' to 'It is now the standard infrastructure.'
— Derived from Gartner’s Top Strategic Technology Trends.
The global "Generative AI in Marketing" market is projected to reach $19.1 billion to $22.02 billion by 2030-2033, growing at a CAGR of 34%–35%. This rapid growth confirms that LLMs are no longer experimental but are becoming core marketing infrastructure. McKinsey (The State of AI in 2025) reports that 88% of organizations are now regularly using AI in at least one business function, with "Marketing and Sales" leading the adoption curve.
Here’s how this growth is expected to redefine the precision of social mining in the coming years:
- Data Mining between the Lines: Businesses will increasingly rely on LLMs' capability to understand context and slang for better contextual reasoning rather than keyword matching, reducing "false positives" in sentiment reports by an estimated 40–50%.
- Solving Information Overload with Narrative Intelligence: By using LLMs to summarize and synthesize massive amounts of social posts, businesses are expected to move beyond simply tracking what is happening and understand the "why"—uncovering the deep-seated cultural shifts and historical context that drive consumer behavior on social channels.
- Multimodal Social Media Data Mining: Mining tools will now be expected to detect visuals (TikTok, Reels, YouTube) and "listen" to audio to mine data
3. Social Media Data Mining Compliance Landscape
The compliance landscape for social media data mining is evolving rapidly, driven by new regulations and increasing emphasis on privacy and user rights.
The ban on social media platforms and related upcoming regulations across the world (Meta and X banned in China; the potential 2025/2026 U.S. TikTok restructuring; mandatory ban on social media for children under 16 in Australia; X banned for non-compliance with court orders in Brazil) signal that social platforms are becoming legitimate media forms, and therefore, governance will only tighten in the coming years and will shift from simple data protection to the regulation of the algorithms themselves.
Here’s how that will affect the future of social media data mining.
- Mandatory Transparency in Data Collection: The U.S. regulatory landscape remains fragmented, with several states introducing their own privacy laws, each with varying compliance requirements and potential penalties. For example, effective January 1, 2026, new regulations under the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) mandate strict disclosures for Automated Decision-Making Technology (ADMT). The takeaway: you must now provide an opt-out and a clear explanation of the AI’s logic for social data mining.
- Increased Focus on the "Lifecycle" of Data: The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union continues to be a global benchmark, imposing significant fines for violations, such as the record-breaking €1.2 billion fine issued to Meta in 2023. The EU's Digital Services Act (DSA) and AI Act introduce additional regulations impacting social media operations. Furthermore, updates to the GDPR in 2025 aim to simplify compliance for SMEs, tighten AI-related rules, and strengthen safeguards for international data transfers, thereby ensuring a more robust privacy framework.
- Proactive Compliance Monitoring: The UK Online Safety Act (OSA) is fully operational as of late 2025. That means platforms and data miners must now proactively identify and remove "priority illegal content" to avoid massive fines.
- Consent Trails for Data Scraping: India’s Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023, now mandates "Consent Managers"—independent platforms that help users manage their permissions. For miners, this means "scraped" data without a clear, verifiable consent trail will become a toxic asset that cannot be legally used.
End Note
Social media data mining has moved beyond counting "likes" and entered the era of predicting human intent. As we navigate a "Splinternet" of fractured platforms and tightening global regulations, the businesses that flourish will be those that view social data not as a collection of posts, but as a real-time map of cultural evolution.
The tools, techniques, and trends outlined in this guide are your bridge to that future. In case you need more support, you can consult a data mining service expert from our team at info@suntecindia.com.
Frequently Asked Questions
For analyzing social media data, raw data are collected from various social media platforms, which are then preprocessed to make them fit and easier for analysis. Various analytical techniques may be used to discover hidden trends and patterns. The techniques include clustering, regression, classification, and association.
Social media data mining works by collecting data from social media platforms by using APIs and web scraping tools. These data are then cleaned, analyzed, and interpreted for actionable insights.
The first step of social media data mining is the collection of data. Depending on the objective of the social media mining, the social media platform of choice is selected, and data is extracted using suitable tools or techniques.
This is done through sentiment analysis. It involves collecting public opinion from social media on brands, products, or specific topics and analyzing whether it is positive, negative, or neutral.
The primary hurdle is Big Data—specifically the sheer volume, speed (velocity), and variety of information generated every second. Additionally, Data Quality is a major issue, as analysts must sift through “noise,” misinformation, and unstructured text to find value.

