
While algorithmic innovation once defined AI progress, the next leap in this market hinges on high-quality training data: data that’s accurately labeled, diverse, and contextually rich.
Organizations are recognizing that data annotation—the process of labeling raw data so that AI systems can interpret and learn from it—has become the invisible engine powering modern machine learning.
The global AI training dataset market reflects this momentum. Market projections from Grand View Research indicate a significant surge in the AI training dataset sector – valued at $2.60 billion in 2024, expected to reach $8.60 billion by 2030, projected at 21.9% annual growth rate. driven by the exponential adoption of AI and machine learning across sectors. The surge underscores a simple truth: the quality, diversity, and precision of labeled data now determine whether an AI model will perform accurately —or fail silently in production.
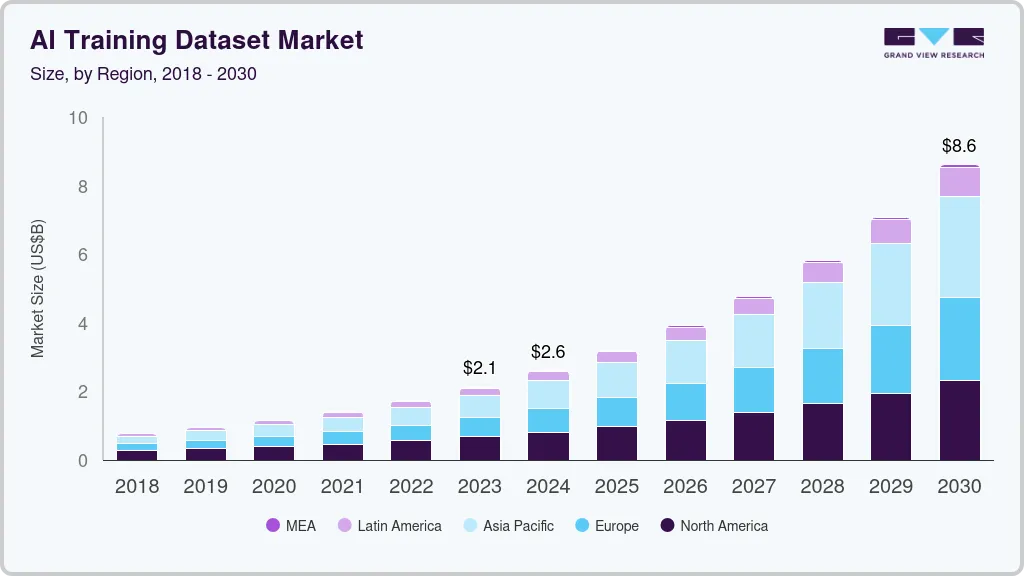
Table of Contents
- The Global Pivot toward Data-Centric AI
- Why Data Annotation Matters: The Invisible Infrastructure of AI Accuracy
- The Key Challenges in Data Annotation: Why High-Quality Labels Are Hard to Produce at Scale
- The Growing Complexity of Multi-Modal Data Annotation
- Data Annotation for Generative AI: Why GenAI Increases Annotation Needs & Complexity
- Automated Data Annotation Systems: Where They Hit and Where They Miss
- The Rise of HITL (Human-in-the-Loop) Data Annotation
- The Market Landscape: Growth, Size, and Investment Trends in Data Annotation
- Future Trends: Automation + Human Expertise + Platform Intelligence
- Bringing It All Together: Businesses Need Accurate Data Annotation for Successful AI Implementation
- FAQs
The Global Pivot toward Data-Centric AI
For years, AI innovation revolved around perfecting algorithms; that paradigm is collapsing now. From globally recognized leaders in AI like Andrew Ng to leading research labs now argue that enterprises can achieve greater accuracy improvements by refining their training data than by endlessly tweaking model architectures.
Instead of focusing on the code, companies should focus on developing systematic engineering practices for improving data in ways that are reliable, efficient, and systematic. In other words, companies need to move from a model-centric approach to a data-centric approach.
— Andrew Ng, CEO and Founder of LandingAI
Model-Centric AI versus Data-Centric AI
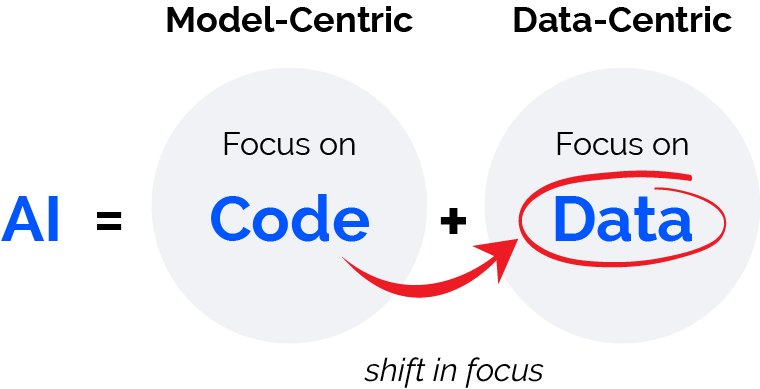
A data-centric approach differentiates itself by continuously improving data quality to sustain AI model performance, while keeping the model and code static. It focuses on iterative data refinement to achieve superior and more reliable model outcomes. In contrast, model-centric AI focuses on optimizing algorithms, assuming data quality remains fixed, which may limit long-term performance improvements.
The data-centric AI movement has gained momentum across leading institutions and companies:
- MIT’s first-ever Data-Centric AI course, developed by Curtis Northcutt and colleagues, focuses on improving machine learning models by enhancing datasets and teaching practical techniques for addressing common data issues in real-world applications.
- Google Brain’s research on ‘Technical Debt in ML: A Data-Centric View’, led by D. Sculley (director in Google Brain), identified data quality as a primary source of long-term system costs.
- Stanford HAI advances AI research, education, and policy with a focus on human-centered technologies, empowering leaders to create AI that benefits society and guides global AI governance.
- ETH AI Center unites AI researchers across departments, promoting excellence, innovation, and entrepreneurship to develop trustworthy, inclusive AI systems.
Why Enterprises are Shifting from Model-Centric to Data-Centric AI
There are several converging factors that are driving this pivot toward data-centric AI:
- Generative AI adoption: Large language and vision models (LLMs, diffusion models) demand enormous, well-labeled datasets.
- Unstructured data explosion: Over 80% of enterprise data is unstructured (like emails, images, or social media posts), requiring data annotation for that data to be machine-readable.
- AI readiness gaps: As Infosys BPM highlights, 59% of tech companies cite immature data management as a key barrier to AI adoption.
- Human-in-the-loop (HITL) strategies: Through human oversight, enterprises are ensuring that data annotations are contextually accurate, which is crucial when dealing with unstructured data that may be ambiguous or nuanced.
Why Data Annotation Matters: The Invisible Infrastructure of AI Accuracy
Behind every breakthrough AI product lies an ocean of labeled data—most of it unseen, yet indispensable. In supervised learning, data annotation is foundational to model accuracy, reliability, and ethical performance.
The Annotation-to-Accuracy Chain
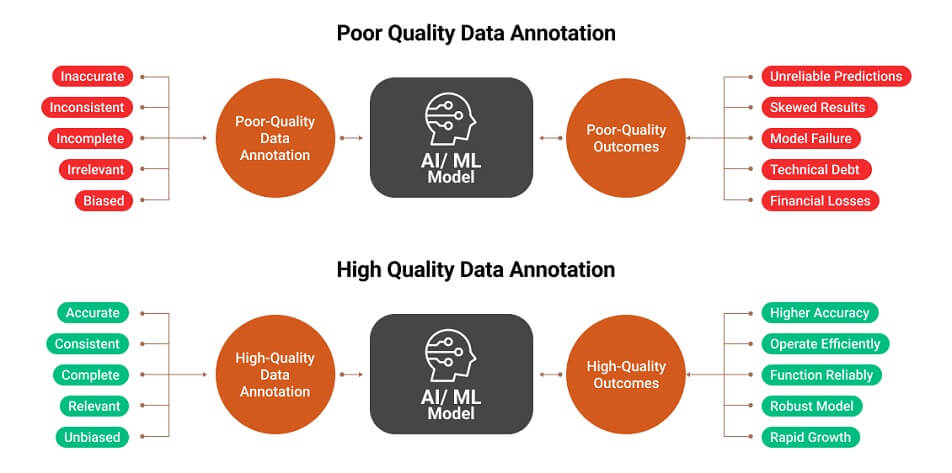
The performance of an AI model can be traced back to a single root: The quality of its annotated data.

If the annotation process introduces bias, inconsistency, or ambiguity in the AI training data, the resulting model will replicate those flaws—a risk with tangible business and ethical consequences across all industries—with particularly severe implications in high-stakes environments where errors can compromise safety or trigger significant financial loss, like healthcare, finance, or autonomous systems.
Benefits of Accurate Data Annotation for AI Models
Accurate text, image, or video annotation doesn’t just improve models—it improves business outcomes:
- Higher AI reliability: Reduces false positives and misclassifications.
- Faster model validation: Reduces retraining time through well-structured datasets.
- Regulatory compliance: Ensures transparency and ethical governance.
- Customer confidence: Builds trust through unbiased, explainable AI decisions.
This is the invisible infrastructure that holds up all AI systems
Poor Annotation = Predictable Failure
Conversely, weak annotation pipelines often lead to:
- Misclassification in safety-critical use cases (e.g., self-driving systems)
- Model drift due to inconsistent labels
- Escalating costs from repeated annotation cycles
- Biased predictions undermining brand reputation
- Loss of user confidence
The cost of low-quality labeling can exceed total AI lifecycle expenses multiple times. Gartner research consistently highlights major financial impacts from poor data quality, with figures around $12.9 million annually lost by organizations, a problem intensified in 2025 due to complex data environments, AI, and cloud growth. Hence, data annotation isn’t just a technical function—it’s a strategic necessity.
The Key Challenges in Data Annotation: Why High-Quality Labels Are Hard to Produce at Scale
Despite technological progress, achieving consistent, high-quality data annotation at scale remains one of the toughest operational challenges. This is due to the complexity of diverse data types, subjectivity, large data volumes, time and resource constraints, the need for consistency across annotators, quality-control requirements, and the specialized expertise required for certain domains.
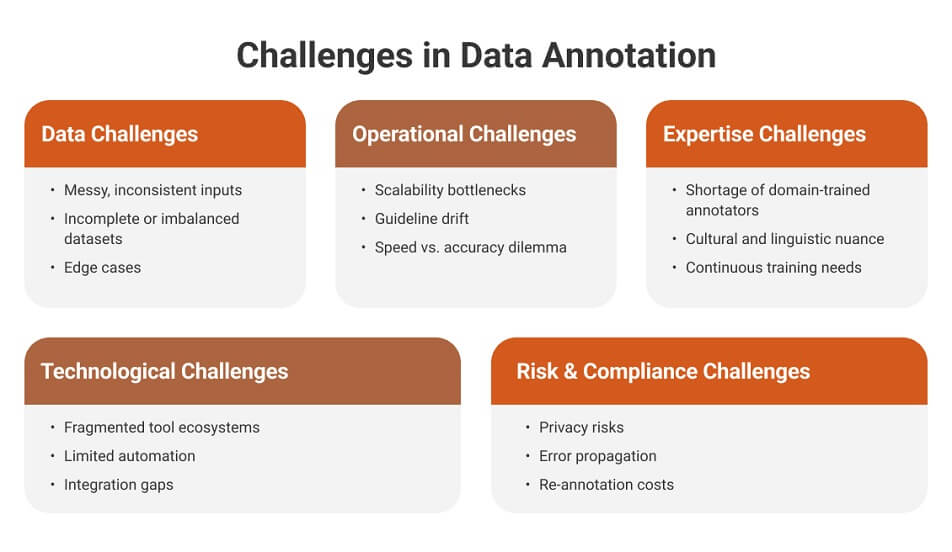
1. Data Challenges
- Messy, inconsistent inputs: Data collected from multiple sources (e.g., IoT sensors, cameras) often lacks a uniform structure.
- Incomplete or imbalanced datasets: Skewed samples lead to model bias.
- Edge cases: Rare events—such as accidents in autonomous driving—require significantly more annotation effort to ensure the model effectively learns to recognize these infrequent but critical scenarios.
2. Operational Challenges
- Scalability bottlenecks: Large projects require managing thousands of annotators simultaneously.
- Guideline drift: Without consistent documentation, annotators interpret labeling instructions differently.
- Speed vs. accuracy dilemma: Faster turnaround often sacrifices quality, impacting downstream AI reliability.
3. Expertise Challenges
- Shortage of domain-trained annotators: Especially acute in fields like radiology, finance, and robotics.
- Cultural and linguistic nuance: Critical in text and sentiment annotation.
- Continuous training needs: Annotation guidelines evolve as models learn, requiring retraining of annotators.
4. Technological Challenges
- Fragmented tool ecosystems: Many organizations rely on disconnected tools for labeling, QA, and workflow management.
- Limited automation: Auto-labeling systems struggle with ambiguous or unstructured data.
- Integration gaps: Annotation platforms often fail to integrate smoothly into MLOps pipelines.
5. Risk & Compliance Challenges
- Privacy risks: Outsourcing data labeling without proper oversight and governance can expose sensitive or confidential information, increasing the risk of privacy violations.
- Error propagation: Early-stage labeling errors compound in later training stages.
- Re-annotation costs: Fixing low-quality labels post-deployment can be very expensive.
The Growing Complexity of Multi-Modal Data Annotation
Data Annotation Methods for AI Models
| Data Type | Annotation Methods | Primary Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Text Annotation | NER (Named Entity Recognition), Sentiment, Intent, Relationship Extraction | NLP, Chatbots, Document Analysis |
| Image Annotation | Bounding boxes, Polygons, Semantic Segmentation | Computer Vision, Retail, Healthcare |
| Video Annotation | Frame-level Labeling, Object Tracking, Temporal Segmentation | Surveillance, Autonomous Vehicles |
| 2D and 3D Image Annotation | Cuboids, Point Cloud Segmentation, LiDAR Labeling | Robotics, Autonomous Navigation |
| Audio Annotation | Speech Transcription, Sound Event Tagging | Voice Assistants, Customer Service Analytics |
Understanding the strategic importance of data labeling for successful AI solutions is only the first step. The next challenge is operational: managing the exponential complexity that arises when AI systems process multiple data types simultaneously. AI now learns not only from text but also from an interconnected web of images, audio, video, 3D sensor data, and more—each requiring a distinct labeling approach.
However, real-world data is rarely perfect. It’s messy, inconsistent, and incomplete—leading to challenges such as:
- Low light or occlusion: 2D image annotation often gets complicated due to obscured objects in imagery.
- Motion blur and object overlap: In video annotation, these distort tracking accuracy, making it harder to identify and label individual elements.
- Sparse or noisy point clouds: When spatial data is incomplete or contains noise, it impacts the accuracy of object recognition and mapping.
- Ambiguous text segments: In sentiment or intent-based text annotation, contextual misunderstandings can lead to misinterpretation, especially with vague or unclear text.
Data Annotation for Generative AI: Why GenAI Increases Annotation Needs & Complexity
Generative AI (GenAI) has dramatically expanded the scope and complexity of data annotation. Unlike traditional AI, which typically focuses on structured data tasks like classification, GenAI models generate original content—such as text, images, and audio—introducing new layers of complexity that require more nuanced annotation.
The need for specialized data annotation for generative AI models is driven by several key factors:
- Diverse and Vast Datasets: GenAI models require extensive, multimodal datasets, including text, images, and audio. Annotators must ensure that these large, unstructured datasets are balanced, accurate, and representative of the real world.
- Complexity of Outputs: GenAI models produce creative and often subjective content, making it essential for human annotators to validate aspects such as tone, style, factual accuracy, and relevance. This shift moves annotation from simple labeling to detailed content validation.
- Focus on Quality Over Quantity: GenAI often operates in less predictable, open-ended domains, increasing potential for both innovation and error. To keep the outcomes relevant, accurate, and ethically appropriate, it is vital to prioritize quality over sheer volume.
- Need for Domain Expertise: As the use of GenAI grows in specialized industries such as healthcare and finance, the need for annotators with deep subject-matter knowledge also increases. In this case, the labeled data must adhere to industry-specific standards, regulations, and practices, as errors or inaccuracies could have severe consequences.
- Ethical Considerations: In the GenAI context, ethical considerations are more pronounced because the content these models generate could be widely disseminated or have far-reaching societal effects. To build ethical GenAI systems (fair, accountable, inclusive, free from harmful stereotypes, and transparent), data annotation workflows must include efforts to detect and mitigate biases in training data.
Automated Data Annotation Systems: Where They Hit and Where They Miss
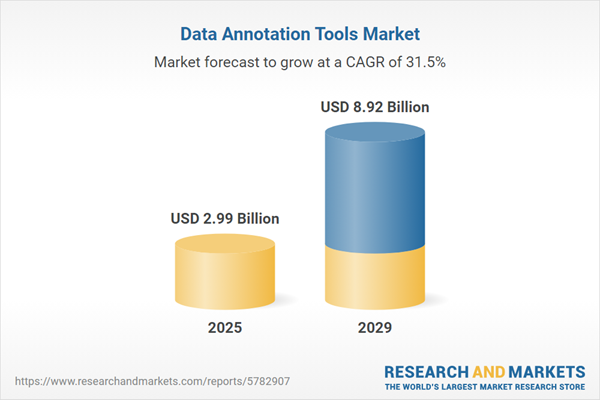
Auto-labeling, or AI-assisted annotation (a process in which AI is used to label the data that trains future AI), is gaining mainstream adoption. The automated data labeling segment is expected to grow at a 33.2% CAGR between 2025-2034, significantly outpacing manual labeling, reports Precedence Research.
Here’s how it helps – instead of drawing a complex polygon around a car pixel-by-pixel, an AI suggests the shape. The human merely clicks “Approve” or “Adjust.” Additionally, the AI identifies the most difficult data points (edge cases) to annotate and sends them to humans for review, while labeling the “easy” data it already understands.
Automated data annotation also thrives because it simplifies model training in cases where real-world data is too limited, rare, or sensitive (such as in medical emergencies) by generating synthetic data. It generates “fake” but physically accurate 3D environments where the labels are automatically “perfect” because the computer created the scene itself.
But, AI-Assisted Data Annotation is Not Yet Fool-Proof

A March 2025 McKinsey report (surveying activity up to that point) confirms that 27% of organizations using generative AI (gen AI) have employees review all content created by the AI before it is used. This is further supported by the state of the data annotation market, which still appears to favor human involvement in labeling workflows — the data annotation services segment held the largest market share of 57.20% in 2024. It is also expected to reach USD 4,068.76 million by 2032.
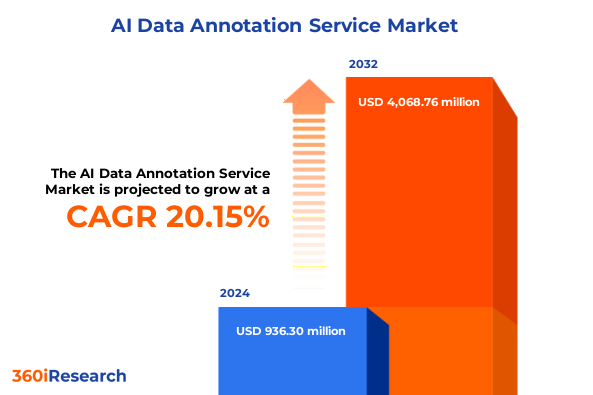
The Rise of HITL (Human-in-the-Loop) Data Annotation
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) annotation integrates the best of both worlds—machine efficiency with human judgment—creating a closed feedback loop that continuously refines data accuracy. Humans can understand nuances, ambiguity, and context in data—elements that automation alone cannot fully grasp.
How HITL Works for Data Labeling
A HITL pipeline follows an iterative sequence designed to improve both data and model quality progressively:
- Guideline Creation: Clear annotation standards are drafted, defining class boundaries, labeling rules, and quality expectations.
- Pilot Testing: Small data samples are annotated and reviewed to calibrate quality metrics and validate feasibility.
- Annotator Training: Human annotators are trained on task-specific guidelines and edge-case handling.
- Annotation & ML Assistance: AI provides label suggestions, which humans verify or correct.
- Quality Assurance (QA): Multi-layer QA checks ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Consensus Scoring & Final Audit: Discrepancies are resolved through reviewer consensus, creating a “golden dataset” for training.
This workflow not only increases precision but also creates feedback loops that continuously enhance model performance.
Benefits of HITL Data Annotation
HITL is not optional; it’s essential, especially in high-risk environments such as autonomous driving, medical imaging, or financial compliance.
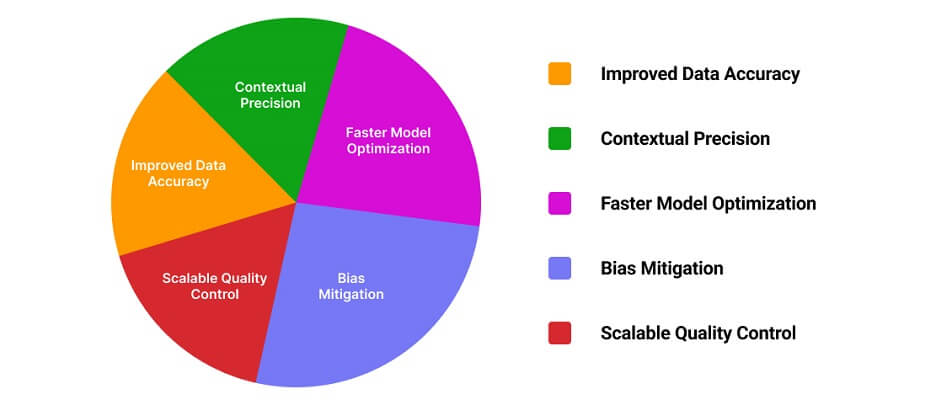
- Improved Data Accuracy: Continuous human oversight minimizes model drift.
- Contextual Precision: Human annotators capture subtleties that automation misses.
- Faster Model Optimization: Real-time feedback accelerates model learning cycles.
- Bias Mitigation: Diverse annotation teams help reduce systematic labeling bias.
- Scalable Quality Control: HITL frameworks support ongoing QA even as datasets expand.
The Market Landscape: Growth, Size, and Investment Trends in Data Annotation
Fueled by soaring demand for high-quality data to train AI and ML models, the global data collection and labeling market is poised for rapid expansion. Valued at $3.77 billion in 2024, the market is projected to reach $17.10 billion by 2030, reflecting a strong Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 28.4% from 2025 to 2030, according to Grand View Research.
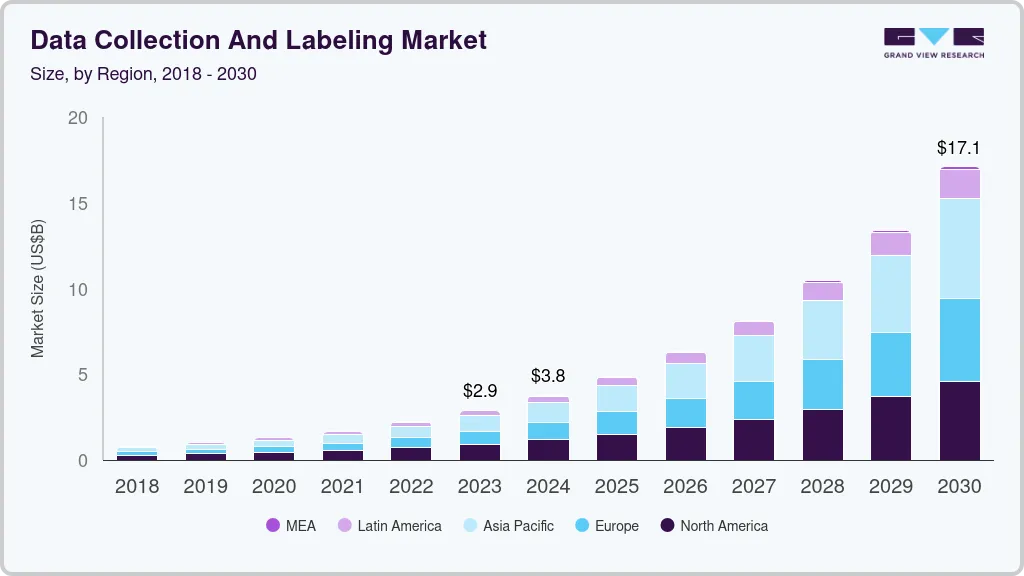
This overall market expansion in data collection and labeling is driving significant demand for specialized tools. According to a study conducted by Global Market Insights, the data annotation tools market was valued at USD 1.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to cross USD 25 billion by 2032.
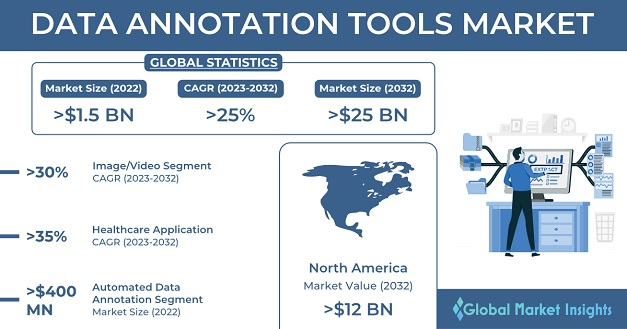
This rapid growth is attracting significant strategic attention and investment. Now, companies are moving beyond simple labeling processes to forge powerful partnerships and implement advanced technological solutions that promise to redefine scalability and efficiency.
- Appen × AWS: Appen partnered with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to enhance AI data sourcing, annotation, and model validation through AWS’s cloud infrastructure.
- Labelbox × Google Cloud: Google Cloud partnered with Labelbox to provide scalable human evaluation for LLMs within its generative AI platform.
- CloudFactory: CloudFactory launched accelerated annotation, combining AI-assisted labeling with human expertise to deliver high-quality data annotation up to five times faster.
These investments indicate a clear trajectory: Annotation is no longer a backend function but a strategic differentiator in AI innovation.
Future Trends: Automation + Human Expertise + Platform Intelligence
As the data ecosystem evolves, the future of data annotation lies at the intersection of automation, human expertise, and intelligent platforms. The annotation process—once seen as a purely manual task—is now evolving into a sophisticated, technology-driven workflow that combines AI-assisted labeling, active learning, and secure data management frameworks.
1. Automation-Driven Labeling
Modern data annotation tools are integrating automation at every stage of the labeling process.
- Auto-Labeling: ML models generate initial labels for humans to validate, speeding up annotation cycles.
- Smart Polygons and Interpolation: For image and video annotation, tools automatically predict object boundaries and transitions across frames.
- Model-Based Pre-Labeling: Pre-trained AI models suggest annotations for repetitive patterns, significantly improving efficiency.
However, automation works best when paired with human-in-the-loop data annotation to manage exceptions, ensure quality, and correct algorithmic drift.
2. Active Learning Pipelines
Active learning enables AI systems to identify uncertain or ambiguous samples and request human intervention only where necessary.
- Reduces redundant labeling efforts.
- Prioritizes edge cases that improve model generalization.
- Cuts annotation cost.
3. Unified Data Annotation Platforms
Enterprises are moving toward platform intelligence—unified systems that connect data ingestion, labeling, QA, and integration into a single pipeline. The key benefits include:
- Centralized project visibility across modalities (text, image, video, 3D).
- Seamless integration with MLOps tools for model training and validation.
- Collaborative workflows enable remote teams to annotate and review data simultaneously.
4. The Rise of Secure and Compliant Annotation
With growing privacy regulations (GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA), enterprises are investing in secure data annotation services that ensure compliance across global operations. Modern platforms now include:
- PII/PHI redaction tools for sensitive data.
- Controlled access environments for annotators.
- Audit trails that maintain transparency in every annotation action.
Bringing It All Together: Businesses Need Accurate Data Annotation for Successful AI Implementation
According to PwC research, AI will drive a 15% increase in global GDP by 2035. This highlights that businesses across the globe are going to utilize AI in one or more ways to drive growth and efficiency. The global AI adoption trend will drive demand for accurate, reliable data annotation, as evidenced by Infosys BPM’s prediction that the data labeling market alone is expected to reach USD 12.75 billion by 2030.
So, if businesses are planning to adopt AI models, how can they annotate data for model training? They can either establish an internal team or outsource data annotation services.
Comparative Snapshot: In-House vs. Outsourced Data Annotation
| Criteria | In-House Annotation | Outsourced Annotation |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Setup Cost | High (infrastructure, tools, training) | Low (pre-established infrastructure) |
| Scalability | Limited by the workforce | Easily scalable |
| Quality Assurance | Requires dedicated QA teams | Built-in multi-layer QA frameworks |
| Time-to-Delivery | Slower; dependent on internal capacity | Faster; optimized for large-scale projects |
| Expertise Diversity | Restricted to internal skill sets | Access to global domain experts |
Why Outsourcing is a Better Choice
Building internal annotation capabilities is resource-intensive. It requires skilled annotators, domain-specific expertise, scalable tools, and robust quality frameworks. For most enterprises, partnering with a specialized data annotation company is the best way forward.
- Scalability on Demand
- Domain Expertise
- Cost Efficiency
- End-to-End Project Management
- Comprehensive QA Frameworks
- Data Security and Compliance

FAQs
How to ensure data annotation quality?
Maintain strict QA workflows with multi-level reviews, clear annotation guidelines, and human-in-the-loop validation. Use automated checks for consistency and continuous feedback loops to refine accuracy over time.
Why outsource data annotation services?
Outsourcing provides scalability, access to domain-trained annotators, and cost efficiency. It also accelerates project timelines while ensuring quality and compliance through specialized tools and established workflows.
How to choose a data annotation company?
Select a provider with proven domain expertise, ISO-certified security, strong QA frameworks, scalable operations, and experience across diverse annotation types like text, image, and 3D/LiDAR.
How does human-in-the-loop data annotation improve model accuracy?
HITL combines automated pre-labeling with human validation. Humans correct ambiguous cases, reducing model drift and enhancing data quality. This hybrid approach ensures greater accuracy and a deeper understanding of context.
How does SunTec India support AI training data services?
SunTec India offers end-to-end data annotation services, covering annotation for text, image, video, and 3D data. Its HITL frameworks, expert workforce, and secure infrastructure ensure enterprises receive high-quality AI training data at scale.

