
AI has transformed how CRM data is processed—but has not yet guaranteed data quality. Issues like pipeline forecasting errors, misrouted outreach, and compliance exposure persist not because AI is ineffective, but because automated CRM data cleansing and enrichment solutions are often overstated or poorly governed.
Let’s examine where automated CRM data enrichment delivers measurable value, where AI-only approaches to CRM data enrichment break down, and why it is best to rely on hybrid architectures—automated CRM data enrichment for scale, paired with human validation for accuracy and accountability.
Where AI Works Well for CRM Data Cleansing and Enrichment
1. AI Enrichment Succeeds when Attributes are Structured, Redundant, and Publicly Verifiable
AI-driven CRM enrichment performs best when attributes are clearly defined and easy to verify from across multiple external sources. Modern enrichment platforms are therefore built around large-scale aggregation and cross-source validation—not inference or interpretation.
Platforms like Breeze Intelligence (HubSpot’s enrichment engine, formerly Clearbit) exemplify this approach. Drawing from over 200 million company and buyer profiles, the system aggregates overlapping firmographic and technographic signals—industry classification, company size, technology usage, and role metadata—from public, commercial, and proprietary datasets. Because these attributes are standardized and externally visible, AI can populate CRM fields with low ambiguity and predictable accuracy.
Industry data confirms this convergence. A 360ResearchReport (2025) shows that data enrichment tool vendors are standardizing on the same operating model:
- 56% embed AI/ML directly into enrichment workflows
- 42% use predictive techniques to prioritize enriched attributes
- 49% integrate real-time analytics for dynamic segmentation
AI succeeds here because the task is deterministic: structured attributes generate consistent signals, the availability of multiple sources enables data validation, and APIs enable automated refreshes—without requiring human judgment.
2. AI Excels at Attribute Cleansing, Completion, and Normalization
According to Business Research Insights (2025), the shift toward autonomous data hygiene is accelerating, with more than 55% of companies adopting AI-powered data profiling and cleansing solutions to automate error detection and correction.
AI is purpose-built for these mechanical tasks:
- Intelligent Deduplication: Uses probabilistic matching to merge records (e.g., “J. Doe” and “Johnathan Doe”) that standard filters fail to catch.
- Contextual Normalization: Leverages NLP to map varied job titles (e.g., “VP Revenue” vs. “SVP Sales”) into standardized personas for accurate segmentation.
- Format Standardization: Automatically aligns international phone numbers and addresses to global standards (e.g., E.164) without manual intervention.
By automating this foundational cleanup, AI ensures CRM systems are stable enough to support reliable CRM data enrichment and downstream analytics.
3. AI Delivers Its Strongest Advantage in Continuous Signal Monitoring
AI’s most defensible advantage in automated CRM enrichment is continuous change detection at scale. Unlike human teams, AI can monitor hundreds of external data streams simultaneously—making it uniquely effective at tracking fast-decaying business signals.
This matters because CRM decay is costly. Poor data quality contributes to an estimated 20% annual revenue loss (Validity, 2024).
Recent market evidence reinforces why AI-led enrichment is now core to data operations. 360ResearchReports (2025) found that 61% of enterprises improved data accuracy after integrating automation and AI into data enrichment, resulting in:
- 47% improvement in customer profiling, and
- 38% increase in campaign efficiency globally
These gains are driven by AI’s ability to continuously refresh records rather than relying on periodic manual updates.
Why AI wins here:
- Immediate Detection: AI flags funding events, leadership changes, or tech shifts as soon as they are indexed.
- Mechanical Validation: The system instantly cross-references new signals across multiple sources.
- Zero Latency: Updates are pushed to the CRM without waiting for a manual review cycle.
With AI’s refresh cycles, the CRM stays up to date, allowing teams to focus on the high-level GTM strategy rather than manual record maintenance.
Expert Perspective: When AI Gets It Wrong: The Real Cost of Automation without Accountability
Where AI-Only CRM Data Cleansing and Enrichment Breaks Down
Across implementations, AI-driven CRM data enrichment systems fail in predictable ways.
1. Lack of Business Context
Automated CRM data enrichment tools can identify organizational signals—like relationships between parent companies and subsidiaries, mergers, rebranding efforts, and shared purchasing decisions—but they lack the business context to consistently interpret their meaning, like how an organization defines ownership, attribution, and control.
Here, AI often applies generic logic by:
- Treating legal parents as selling entities when subsidiaries own the budget
- Collapsing rebranded or merged entities too early—or too late
- Inferring shared buying authority where decision rights are actually regional or functional
The result isn’t missing data, but plausible misinterpretation—leading to duplicate accounts, misattributed revenue, and pipeline views that look coherent but don’t reflect how the business actually operates.
Business Cost: revenue misattribution & pipeline distortion
- Overstated pipeline value
- Inaccurate forecasts
- Misallocated sales investment
2. Plausibility and Semantic Errors
AI can update CRM records with data that is technically valid but operationally useless or misleading because it doesn’t reflect the real, up-to-date situation, such as:
- AI enriches contact data by pulling in details from external sources, such as social media or company directories. Based on this data, you might link an active sales opportunity to a prospect who was once a decision-maker at their company, but has since left. Therefore, if the sources used by automated CRM data enrichment tools are not updated, the enriched data is pointless.
- AI may pull in job titles, company revenue, or budget data from external sources and link them to CRM records, assuming that someone with a certain title (e.g., “Marketing Manager”) still holds that role and has a certain budget authority. But if the person was promoted, moved to a different department, or left the company, or if the company’s budget allocation has changed, your CRM data, despite being enriched, would be of no use to your sales/marketing campaigns.
- AI learns from patterns across many data points and applies those patterns to enrich CRM data. So it might gather that a company has 500 employees and assume large budgets and mature processes when the company might still be in a growth phase, with tighter budgets, fewer formalized processes, and shorter decision-making cycles.
Salesforce’s State of Data and Analytics (2025) report notes that
89%Data and analytics leaders using AI report inaccurate or misleading outputs. |
84%Data and analytics leaders believe their data strategies need overhauls to succeed with AI. |
54%Business leaders don’t trust their data entirely, citing persistent issues with accuracy, reliability, and relevance. |
55%Data and analytics leaders at companies training or fine-tuning their own models report wasting significant resources due to poor data quality. |
|---|
Business Cost: Wasted sales & marketing efforts
- Lower campaign efficiency
- Reduced conversion rates
- Declining ROI from misdirected outreach
3. Bias and Market Coverage Gaps
A 2025 systematic review by Springer Nature found that generative AI systems consistently reinforce performance gaps when certain regions, languages, or organizational forms are underrepresented in training data. In enrichment use cases, this manifests as models defaulting to assumptions learned from dominant markets, even when those assumptions don’t apply elsewhere.
AI-based data enrichment is only as reliable as the geographic, linguistic, and organizational diversity of the data on which it is trained. When training datasets are concentrated in mature markets—primarily North America and Western Europe—the models learn patterns that reflect those markets’ corporate structures, job taxonomies, naming conventions, and disclosure norms.
When these enrichment models are applied to datasets from emerging or non-English markets, they struggle to interpret the same signals—misclassifying titles, misinferred firmographics, and oversimplified or incorrect account hierarchies. This is not just lower coverage; it is structural distortion.
Business Cost: Missed opportunities in non-core sectors
- Qualified accounts deprioritized
- Delayed market entry
- Direct revenue leakage
4. Compliance Blind Spots
Automated CRM data enrichment systems don’t inherently understand the legal complexities around data protection and privacy. There are certain compliance aspects that AI may overlook (such as lawful basis, proportionality, or regulatory intent), creating “blind spots” where legal requirements are not properly met.
Additionally, under data protection laws like the GDPR, the CCPA, and the EU AI Act (effective 2025), enrichment defensibility depends on governance and human accountability—not on automated inference. So, even if a company uses AI to enrich its CRM system with contact data, it is legally responsible for ensuring that this data enrichment complies with applicable regulations.
Business Cost: Regulatory & compliance risks
- Financial penalties
- Legal exposure
- Operational disruption
- Reputational damage
5. Failure in High-Value Edge Cases
The most valuable CRM records—large enterprises, regulated industries, merger scenarios—are the least pattern-conformant. For instance, large enterprises may have complex organizational structures, with various departments, subsidiaries, or decentralized decision-making processes that are difficult to model. AI either oversimplifies these records or hallucinates by updating fabricated information. Errors here are disproportionately costly.
Business Cost: High-cost errors on strategic accounts
- Misdirected sales strategies
- Missed high-value deals
- Flawed strategic decisions
6. Model Drift over Time
AI models age. As markets shift, models trained on historical data increasingly misclassify intent, relevance, and opportunity health. Without human recalibration, enrichment quality degrades quietly but steadily.
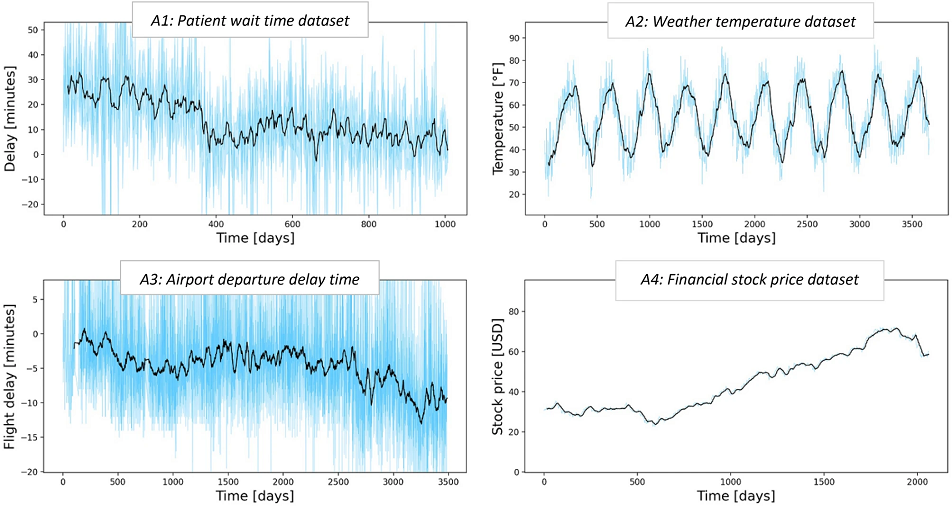
(Source: Nature)
A 2025 research from the AI Governance Library shows that even high-performing models exhibit a predictable increase in error rates over time as real-world data diverges from original training distributions.
Business Cost: Degraded forecasting & GTM effectiveness over time
- Declining pipeline accuracy
- Slower GTM response
- Compounding revenue risk

Why Human-in-the-Loop Data Validation Is Non-Negotiable in Automated CRM Data Enrichment
Automated CRM data enrichment operates at scale—but scale alone does not create trust in data. Once enriched CRM data begins to influence lead routing, account ownership, revenue attribution, compliance posture, and data-driven decisions, AI’s probabilistic accuracy is no longer acceptable. Errors become financial, regulatory, and reputational, not just operational.
This is where Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) validation becomes non-negotiable. High-performing organizations understand this; they design systems in which AI handles repeatable, pattern-based enrichment and humans intervene precisely where judgment, context, and accountability are required.
Human oversight protects the CRM data integrity in areas where automated enrichment consistently fails, by:
- Mapping Complex Corporate Hierarchies: Cross-reference news, press releases, and legal filings to manually map complex mergers or subsidiary spin-offs that AI logic frequently misgroups.
- Investigating Data-Poor “Edge Cases”: For accounts with limited digital footprints—such as private equity firms, stealth-mode startups, or niche industrial players—humans validate data that AI cannot reliably infer from patterns alone.
- Vetting True Buying Authority: Confirm that contacts hold genuine decision-making power and budget control rather than just having a plausible or inflated job title.
- Applying Regulatory and Ethical Judgment: Provide the qualitative judgment required to meet evolving global privacy standards (like GDPR or the EU AI Act) that automated filters cannot interpret.
- Governing Model Integrity and Drift: Perform periodic spot-checks on AI outputs to catch “drift”—where the AI begins hallucinating data—and recalibrate the logic to reflect current market realities.
A 2025 peer-reviewed study published in the International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) shows that AI systems augmented with structured human validation achieve materially higher accuracy than AI-only workflows—particularly in high-risk decision environments.
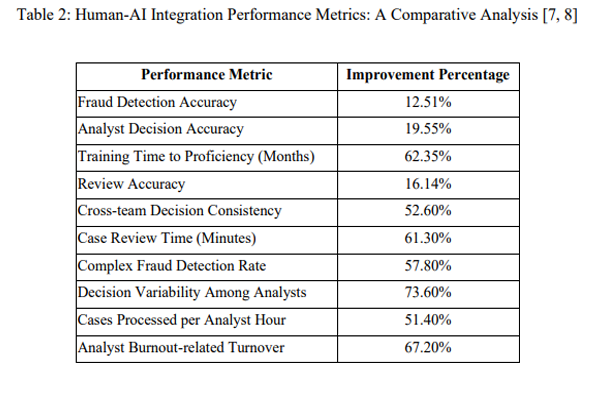
[Source: Ethical AI Frameworks, IJARET 2025 study (Section 4: Human-in-the-loop Integration) ]
A Practical Hybrid Framework for CRM Data Cleansing and Enrichment
McKinsey’s “The State of AI in 2025” research states that the most successful AI implementations are those with the highest level of strategic human involvement.
To get the most from AI-driven CRM data enrichment, follow this structured hybrid approach where AI and human expertise complement each other:
Step 1: Start with a CRM Audit & Data Gap Analysis
Use AI to scan CRM records for missing fields, inconsistencies, duplication, and staleness at scale. The human team identifies which gaps materially affect GTM decisions, filtering out noise to focus on business-critical issues.
Step 2: Normalize First-Party Data
Employ AI to extract, standardize, and reconcile structured first-party data from internal systems (transactions, marketing automation, product usage). Since this data is owned and governed internally, AI can operate with sufficient oversight, and minimal manual review is required at this stage.
Note: This step is data preparation, not enrichment. It establishes a trusted baseline before introducing external signals.
Step 3: Apply Controlled AI-Driven External CRM Data Enrichment
Use AI to append externally sourced attributes (firmographics, technographics, role metadata) only for predefined fields tied to targeting, routing, or segmentation. Here, human teams define what can be enriched, preventing uncontrolled data growth in CRM.
Step 4: Human Validation at Decision-Critical Boundaries
Route high-impact, ambiguous, or compliance-sensitive records to human reviewers. These experts validate account hierarchies, buying authority, executive changes, and regulatory exposure—areas where AI confidence is probabilistic, not absolute.
Step 5: Maintain Governance & Feedback Loops
Maintain audit trails for enriched fields and track where AI required human correction. Use this feedback to tighten AI confidence thresholds, not to eliminate human review.
Step 6: Activate Only Validated Data in GTM Workflows
Ensure only AI-enriched, human-validated records flow into scoring, routing, personalization, and forecasting. This ensures GTM teams act on trusted data, not probabilistic signals.
Actionable Tip for CRM Users
Treat this framework as a repeatable process. Start small with high-priority accounts, refine your AI-human balance, and scale across your CRM to build a resilient, high-confidence GTM data foundation.

The Future of Scalable B2B CRM Data Enrichment: Collaborative Intelligence over Full Automation
In 2026, AI is more capable, but complete automation for complex CRM data enrichment remains impossible as of yet.
Because business reality is inherently messy. Companies reorganize, merge, rebrand, and pivot constantly. AI can’t model this chaos reliably without human oversight for database cleanup and CRM record enrichment.
The EPOCH Framework: What AI Cannot Replicate
MIT Sloan research (October 2025) identified five uniquely human capabilities machines can’t automate:
- Empathy and Emotional Intelligence
- Presence, Networking, and Connectedness
- Opinion, Judgment, and Ethics
- Creativity and Imagination
- Hope, Vision, and Leadership
Without these human layers, AI frequently misinterprets noise as signals.

AI Maturity Model: How to Scale CRM Data Enrichment Responsibly
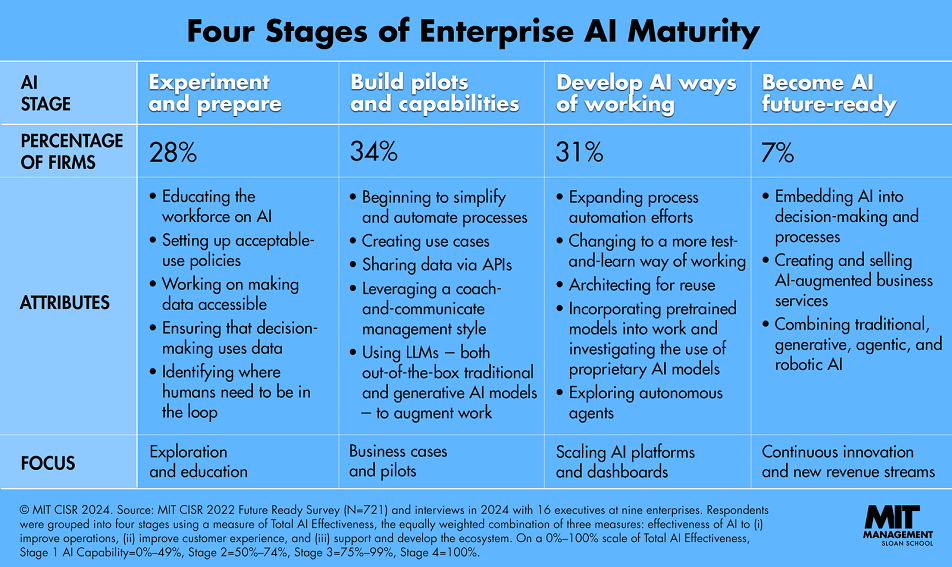
As businesses prepare for automated CRM data enrichment at scale, organizational AI maturity—not the sophistication of data enrichment tools—determines outcomes. MIT’s 2025 analysis (re-examining the CISR Future Ready Survey of 721 enterprises) identifies four predictable stages:
| Stage | Behavior | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Naive Automation | Deploy the best CRM data enrichment tools and assume 100% accuracy | Enriched data assumed as trusted data |
| 2. Disillusionment | Face duplicates, misalignment, compliance gaps | Question ROI, lose sales trust |
| 3. Strategic Hybrid | Add human validation for low-confidence/high-value records | CRM data quality stabilizes |
| 4. Optimized Collaboration | AI handles volume; humans enforce context & compliance | Sustainable, revenue-relevant CRM |
Gartner AI Maturity research (2025) reinforces this trajectory: 45% of high-maturity organizations sustain AI initiatives for more than 3 years, a finding strongly correlated with governance, oversight, and continuous recalibration.
The Current Reality
Most companies are stuck between Stage 2 and 3, i.e., between disillusionment and strategic hybrid execution. The few mature leaders have already moved to Stage 4—treating CRM data enrichment as a precision system in which AI scales execution and humans safeguard business reality.
The Takeaway: Effectiveness of CRM Data Enrichment Depends on Design, Not Tools
AI solutions for automated CRM data cleansing and enrichment are highly effective—within defined boundaries. They transform scale economics and baseline CRM data hygiene, but they cannot replace contextual judgment, regulatory interpretation, or accountability; only human oversight can ensure that.

