
Your CRM is meant to be the central engine driving revenue growth—but many organizations today are discovering that their CRM is actually slowing them down. Contact information becomes outdated, company structures change, and critical fields decay faster than internal teams can update them. The result: missed opportunities, misdirected campaigns, and wasted sales effort.
According to Validity’s 2025 State of CRM Data Management Report, over 37% of CRM users report revenue losses directly tied to poor data quality. This challenge is compounded by structural and organizational limitations—Bain & Company’s 2025 survey found that 70% of companies struggle to integrate their sales plays into CRM and revenue technologies, weakening data reliability for forecasting and undermining effective revenue operations.
These pressures are a major tailwind for CRM data enrichment because teams need faster ways to restore usability and trust in CRM-driven execution and forecasting. But rapid adoption reflects urgency more than maturity: the market is still fragmented, outcomes vary widely, and enrichment alone doesn’t resolve workflow and governance gaps.
The State of CRM Data Enrichment in 2025: Rapid Growth, Lingering Data Gaps
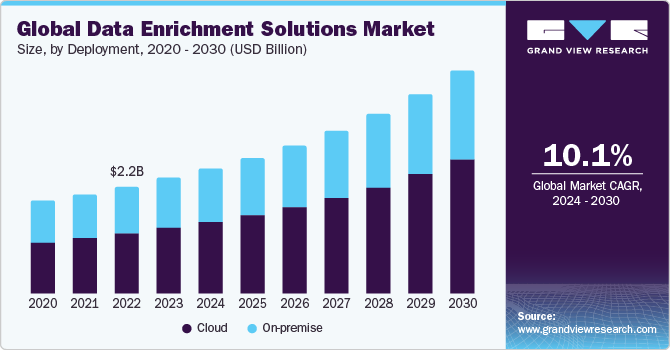
Grand View Research estimates that the global data enrichment market will be valued at USD 4.58 billion by 2030 and will continue to grow strongly, driven by rising demand for CRM data enrichment, contact data enrichment, and business data enrichment across sales, marketing, operations, and customer intelligence functions. Organizations increasingly depend on cloud-based B2B CRM data enrichment platforms (56% and growing), compliant B2B data enrichment services (particularly for SMEs), and newer record enrichment workflows (integrating generative AI and AI/ML with data enrichment processes) to scale audience targeting, customer personalization, and CRM-driven decisions.
Yet this adoption has clearly outpaced its execution discipline. The Validity report notes that, despite treating CRM as a revenue cornerstone, 76% of organizations report that less than half of their CRM data is accurate and complete. This exposes a systemic weakness in how organizations enrich customer and company data—particularly when enrichment relies heavily on tools without structured validation, governance, or continuous monitoring.

These findings define the reality of CRM enrichment in 2025: strong market momentum and widespread reliance on leading CRM data enrichment tools, alongside persistent weaknesses in CRM data integrity.
Benefits of CRM Data Enrichment: Where It Drives Measurable Revenue Outcome
Enriching your CRM platform with verified, relevant, and recent data turns it into a system that actively supports revenue decisions. By updating account, contact, and firmographic data, CRM enrichment ensures that your sales, marketing, operations, and forecasting teams base their decisions on accurate, usable CRM records rather than static or outdated data.
Grand View Research reports that the global data enrichment market was valued at USD 2.37 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.1% through 2030, driven by rising demand for hyper-personalization, data-driven decision-making, and AI-enabled data workflows. While the market spans multiple enterprise functions, sales and marketing teams are realizing this growth most directly through CRM-centric use cases such as improving targeting accuracy, sales productivity, and pipeline reliability.
Let’s see them one by one.
1. Precise B2B Targeting: Fueling Sales Conversions with Data Clarity
Without database cleanup and CRM data enrichment, teams rely on incomplete attributes—missing job roles, incorrect company sizes, outdated contact details—leading to broader targeting and low engagement. The Validity CRM 2025 report, based on insights from 602 CRM users and stakeholders, finds that more than half of CRM data is inaccurate across most organizations, which impacts audience segmentation and personalization.
Enriched firmographics, verified roles, and standardized seniority data allow teams to focus on accounts and buyers that fit their ideal customer profile (ICP), have decision-making authority, and hence, will be more likely to convert.
2. Accelerated Outreach: Powering AI Agents with High-Fidelity Inputs
Sales automation and AI agents are increasingly used to speed up prospecting and outreach. The market continues to welcome new and improved AI solutions for automated CRM data cleansing and enrichment. However, such automation can amplify data problems when CRM records are outdated or incomplete.
While AI can trigger outreach sequences based on user behavior data, verified personas, and accurate intent data, it only works effectively when CRM data is correct. Many AI initiatives have stalled—not due to lack of tools, but due to poor CRM data inputs.
McKinsey’s “The State of AI in 2025” report notes that only 39% of respondents report any EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) impact at the enterprise level from AI. This figure indicates that many organizations are experimenting with AI agents, but in sales operations, their effectiveness depends entirely on the quality of CRM data. Enrichment is what moves these tools from experimentation to real productivity gains.
3. Operational Excellence: Standardized CRM Data Enrichment across Global Teams
As organizations scale across regions and business units, CRM data quality management gets tougher, because data often decays at an incredible rate; it becomes fragmented due to inconsistent data capture and maintenance practices. These operational inconsistencies lead to duplicate records, unreliable reporting, and breakdowns between teams.
CRM data enrichment standardizes account and contact information by normalizing firmographics, roles, and key attributes across the CRM. This ensures that global teams work from consistent, trustworthy records, reducing manual cleanup and improving cross-functional alignment. When data enrichment is applied systematically, CRM workflows scale more reliably, supporting accurate reporting and smoother revenue operations.
4. Pipeline Forecast Integrity: Using Standardized CRM Data Enrichment to Eliminate Revenue Gaps
Pipeline forecasts are only as reliable as the CRM data behind them. Inaccurate CRM data is a leading cause of forecast gaps and missed revenue targets. According to Validity’s State of CRM Data Management 2024, 31% of CRM admins report that poor-quality data costs their company at least 20% of their annual revenue.
Standardized, deduplicated, and enriched CRM data can help eliminate those gaps, improve lead scoring, opportunity tracking, and forecast confidence.

Top B2B CRM Data Enrichment Tools: Capabilities and Structural Limits
As CRM data decay has become a recognized revenue risk, a broad ecosystem of B2B data enrichment tools has emerged to fill the gap. These platforms promise real-time updates, deeper customer insights, and scalable data completeness across sales and marketing systems.
Broadly, today’s CRM enrichment landscape can be grouped into four dominant categories, each offering clear benefits—but also carrying structural limitations that prevent them from delivering sustained CRM data accuracy on their own.
1. B2B Contact Data & Firmographic Enrichment Platforms
Examples: ZoomInfo, Apollo, Clearbit, Lusha, Cognism
These tools focus on appending missing contact and company attributes, such as:
- Job titles and seniority levels
- Company size, industry, and revenue estimates
- Email addresses and phone numbers
- Basic technographic indicators
Benefits
- Fast, API-driven record enrichment at scale
- Strong coverage for outbound sales and ABM use cases
- Easy CRM integrations for automated record updates
Limitations
Despite their popularity, these tools primarily rely on aggregated third-party datasets that age quickly. Job changes, role shifts, and company restructures often lag real-world updates by weeks. More critically, enrichment logic is probabilistic, not definitive—meaning records are “likely correct,” not verified. Duplicate contacts, misaligned account hierarchies, and incorrect role assignments still persist, especially in mid-market and global datasets.
These platforms enrich volume, not certainty.
2. B2B Data Appending & Identity Resolution Tools
Examples: Experian, Dun & Bradstreet, Melissa, People Data Labs
Identity Resolution Tools connect fragmented customer data from various sources (websites, apps, CRM) to create a single, unified profile for an individual, solving the “same person, different data” problem.
These IR tools solutions specialize in:
- Data standardization and normalization
- Identity resolution across fragmented datasets
- Business registry and firmographic verification
Benefits
- Improved consistency in account naming and firmographics
- Strong compliance and governance alignment
- Useful for data deduplication and master data management
Limitations
While these tools improve structure, they often lack deeper contextual accuracy. They can confirm that a company exists—but not whether the right buyer, decision-maker, or active contact is associated with the opportunity. They are excellent at what the data is, but not whether the data is relevant or current for revenue execution.
3. AI-Driven CRM Data Enrichment & Predictive Data Platforms
Examples: Clay, MadKudu, 6sense (enrichment layers), HubSpot AI enrichment
These AI-powered data enrichment tools increasingly promise:
- Automated data completion
- Predictive role inference
- Intent-based enrichment
- Continuous CRM updates
Benefits
- Scalable record enrichment without manual effort
- Ability to infer missing fields using behavioral and pattern-based signals
- Tight alignment with marketing automation and scoring models
Limitations
This AI solution for automated CRM data cleansing and enrichment inherits every flaw of the underlying CRM data. When inputs are incomplete, outdated, or duplicated, AI models amplify inaccuracies rather than resolve them. AI-enriched CRM records are often less accurate, particularly when enrichment runs without human validation checkpoints, thus accelerating data decay instead of stopping it.
4. Real-Time Data Capture & Form Enrichment Tools
Examples: Clearbit Forms, Segment, RudderStack
These tools enrich data at the point of capture by:
- Auto-filling firmographic data from IP or email domains
- Reducing friction in inbound lead capture
- Improving initial data completeness
Benefits
- Cleaner inbound data from the start
- Higher form completion rates
- Better early-stage lead qualification
Limitations
Point-of-entry enrichment does nothing to fix:
- Existing CRM data debt
- Post-conversion data decay
- Role changes after capture
- Account-level inconsistencies over time
They solve entry accuracy, not lifecycle accuracy.
The Core Problem with CRM Data Enrichment Tools
Across categories, most enrichment platforms are designed to move fast and scale wide. Their core strength is automation—not validation.
What they lack is:
- Contextual judgment
- Business-rule awareness
- Exception handling
- Accountability for revenue-impacting errors
This explains why, despite widespread adoption of some of the best CRM data enrichment tools, 65% of organizations still report that their CRM data is somewhat accurate rather than entirely accurate.
And that distinction is critical.
CRM Data Accuracy Ultimately Requires a HITL (Human-in-the-Loop) Framework
Sales and marketing campaigns depend on precision, not approximation. A single incorrect role, outdated contact, or misaligned account can:
- Waste paid media spend
- Trigger compliance risks
- Break personalization
- Distort sales pipeline forecasts
To achieve complete CRM data accuracy, organizations must move beyond tool-only enrichment and adopt a Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) framework for CRM data enrichment—where automation handles scale and human intelligence ensures correctness, relevance, and accountability —thereby maintaining CRM data integrity.
The most effective revenue teams in 2025 are no longer asking:
Which enrichment tool should we use for data accuracy?They are asking:
Where must human validation intervene to protect revenue-critical data?A Proven 5-Stage HITL (Human-in-the-Loop) B2B CRM Data Enrichment Framework

To close the accuracy gap left by tool-only enrichment, responsible organizations adopt structured HITL workflows. These frameworks preserve the speed of enrichment platforms while introducing human validation at revenue-critical points.
Here’s is a practical, field-tested 5-stage HITL framework that our clients often adopt and see results from:
Step 1: CRM Data Audit and “Materiality” Mapping
Conduct a targeted audit to identify missing or outdated data fields. While AI can flag anomalies, human oversight can define materiality—deciding which data points actually drive revenue (e.g., a CEO’s direct dial) versus those that are just “noise” or “vanity metrics.”
Step 2: Establishing the First-Party “Anchor Set”
Consolidate internal sources—transaction history, marketing engagement, and customer support records—before external data enrichment begins. Using first-party data as a human-authored anchor set resolves a significant portion of gaps and prevents AI from hallucinating firmographic details.
Step 3: Targeted External CRM Data Enrichment via “Tiered Tools”
Fill remaining gaps using the best CRM data enrichment tools, such as Experian (SME-focused) or ZoomInfo (Enterprise). The best practice is to focus only on high-impact attributes: verified email addresses for deliverability, job functions for personalization, and revenue data for territory prioritization.
Step 4: Expert Validation: Human Intelligence as the Final Quality Filter
Human reviewers validate enriched records for:
- Contextual plausibility
- Correct buyer relevance within account hierarchies
- Regulatory and regional appropriateness
- Edge-case errors that AI models consistently miss
This human-led intervention serves as the final filter, transforming “likely correct” automated outputs into high-fidelity, decision-grade intelligence.
Step 5: Governance, Integration, and Continuous Data Drift Monitoring
Integrate human-validated data into the CRM with audit trails documenting the source, time, and validation method. Employ continuous monitoring—using “Retraining Triggers”—to detect data quality drift as soon as accuracy falls below a set threshold, say 85%.

Top Data Enrichment Trends in 2026: AI, Compliance, and Hyper-Personalization
Not just in 2026, but over the next few years, three converging forces are expected to transform B2B CRM data enrichment from a back-office task into a board-level priority: autonomous agents, regulatory compliance, and the personalization-trust paradox.
1. Autonomous AI Agents Will Reshape CRM Enrichment
The shift from “automation” to “agency” is the hallmark of 2026. According to McKinsey’s 2025 State of AI report, 62% of organizations are already moving beyond static triggers to deploy Autonomous AI Agents
Modern Agentic AI can already:
- Detect job changes by monitoring public profiles, company announcements, and social signals
- Identify funding events or mergers in near real time
- Infer buying intent from content consumption, product usage signals, or web behavior
- Trigger automated CRM updates, routing changes, or outreach workflows without human initiation
Understand better with real-world Agent AI implementations:
| Claygent (Clay) | 11x (Alice) | Artisan (Ava) |
|---|---|---|
| A pioneer in “Waterfall Enrichment.” Instead of relying on a single source, Claygent uses GPT-4 to sequence searches across 75+ providers (such as Apollo, Hunter, and PeopleDataLabs) until it finds a verified match. If a prospect leaves their company, Claygent can autonomously find their new LinkedIn role, verify their new work email, and automatically update CRM. | An autonomous SDR agent that acts on the enriched data. Alice monitors “Trigger Events”—such as a target account raising a Series C or hiring a new VP of Sales—and instantly enriches the record with these context clues, then drafts a 1:1 personalized email based on the latest funding data. | This is Account-Level Intelligence. Ava can research a company’s recent 10-K filings or quarterly earnings calls to extract strategic priorities, enriching the CRM with “Business Pain” data points that traditional firmographic tools miss. |
These capabilities fundamentally change enrichment from a batch process into a living data layer. However, without high-fidelity CRM data, these agents risk “hallucinating” account hierarchies, which can lead to automated sales blunders.
2. Compliance Will be Seen as a Quality Filter: Navigating Global Regulations by Design
By 2026, the EU AI Act and evolving GDPR standards will shift the burden of proof from what data you have to how it is justified. Compliance will no longer be a legal hurdle; it will be a must-consider data-quality filter. PwC’s 2025 Responsible AI Survey confirms that 58% of executives now see these governance measures as direct drivers of ROI and operational efficiency—not just regulatory safeguards.
Different enrichment tools have taken different paths to solve this:
- ZoomInfo: Combines machine learning with a community-powered network, providing detailed audit trails and self-service portals for data subjects to manage their profiles, ensuring transparency at an enterprise scale.
- Cognism: Differentiates itself by scrubbing mobile numbers against National Do-Not-Call (DNC) registries across 14 countries (compared to the standard 8). For global teams, this makes compliance a proactive driver of sales productivity rather than a reactive legal risk.
- Ocean.io: Uses “Legitimate Interest” as a data-quality filter, indexing hundreds of millions of websites to ensure enrichment is based on publicly available professional life, minimizing the risk of “creepy” or non-compliant personal data use.
- Lusha: As the only sales intelligence tool accredited under ISO 27701 (an international privacy standard), Lusha uses third-party-audited “Privacy-First” sourcing to ensure that enriched data is legally defensible for enterprise-scale outbound.
Moving on, companies that proactively engineer compliance into their data enrichment architecture will scale revenue with confidence, while others will be forced to slow down under growing regulatory scrutiny.
3. Trust-First Personalization Will Define The Next Phase of B2B Sales Intelligence
Salesforce Research 2025 indicates a staggering leap: 73% of buyers now expect hyper-personalized treatment—nearly double the sentiment from just two years ago. However, this demand for intimacy comes with a strict caveat: 71% of customers are more protective of their data than ever before.
This creates a high-stakes “paradox” where buyers are willing to trade their data for value, but only if the recipient proves they are a responsible steward. In 2026, customer trust will shift from a “legal checkmark” to a primary driver of brand equity. Therefore, businesses must lead with how they protect consumer data, not just how they use it.
4. The 2026 Standard: Zero-Error CRM Data Enrichment
CRM data enrichment will be measured less by data volume and more by data correctness. As this data feeds forecasting models, territory planning, revenue attribution, and executive reporting, even slight inaccuracies—misaligned account hierarchies, incorrect ownership mappings, or outdated firmographics—can compound into operational errors.
The idea of zero-error CRM data enrichment does not imply perfection at capture, but continuous correction at scale. This standard will require systematic deduplication, cross-source reconciliation, enrichment confidence scoring, and post-enrichment validation for high-impact records. Organizations that achieve this will operate with cleaner pipelines, more reliable forecasts, and higher confidence in CRM-driven decisions.
Conclusion: CRM Data Enrichment Success Is Architectural
CRM data enrichment is no longer a tooling problem (i.e., “What software can I buy to clean my data?”); it has become an architectural challenge (i.e., “How do I build a permanent system where data is always clean and updated?”).
Organizations that treat enrichment as a “set and forget” feature will struggle with the inevitable data decay. Those that implement a governed, human-in-the-loop architecture for CRM data enrichment will transform their CRM from a static database into a durable, strategic engine for growth.
The question for 2026 is no longer: ‘Is our CRM data accurate?’ but rather: ‘Is our CRM data enrichment workflow resilient enough to keep it that way?’

