
Go-to-market (GTM) success depends on how accurately GTM teams understand and engage with their target audience. Every decision—whom to target, when to engage, and which accounts need to be prioritized—relies on the quality of CRM data.
Yet even with the most sophisticated tools, such as marketing automation, sales engagement platforms, and ABM software, many GTM teams struggle to convert leads, accurately forecast pipelines, and reach the right buyers. The issue isn’t the tools—it’s the data powering them.
When CRM records contain incomplete firmographics, outdated contact details, or missing intent signals, GTM strategies operate without clear visibility. According to Validity’s State of CRM Data Management 2025 report, based on insights from 602 CRM users and stakeholders, 37% of CRM administrators report that poor-quality data leads to significant revenue loss. That’s not a data issue—it’s a business crisis.
CRM data enrichment—the systematic process of cleansing and enriching CRM data with verified, relevant external datapoints—has emerged as the foundation for high-performing GTM teams, turning the CRM from a static repository into an intelligence engine that supports revenue decisions across sales, marketing, and operations.
Understanding CRM Data Enrichment as a GTM Enabler
CRM data enrichment goes well beyond basic database cleanup, like deduplication or fixing formatting errors. It involves layering strategic intelligence onto your existing CRM records, like:
- Updating validated contact information, such as accurate email addresses and phone numbers (contact data enrichment)
- Enriching company records with firm-level firmographics, including organization size, revenue, and industry classification (company data enrichment)
- Adding technographic insights that reveal the tools, platforms, and systems currently in use (tech-stack data enrichment)
- Appending buying-intent data that signals active research, engagement patterns, and purchase readiness (behavioral data enrichment)
For GTM strategists, this distinction matters. Simple database cleanup removes friction; CRM data enrichment creates opportunity.
Four Ways CRM Data Enrichment Transforms GTM Strategies
CRM data enrichment strengthens GTM strategies by injecting real-time intelligence into sales records:
- Who do you target?
- When do you engage?
- How fast do deals move?
- How accurately is revenue forecasted?
When enrichment is applied systematically, it aligns marketing, sales, and RevOps around a shared, reliable view of the market rather than fragmented assumptions.
1. Precision Targeting: Moving from Broad Segments to ICP (Ideal Customer Profile) Alignment
Enrichment-prior GTM strategies fail most often at the targeting stage. The marketing team casts too wide a net, the sales team pursues accounts outside the ideal customer profile, and both teams wonder why conversion rates remain stubbornly low.
B2B data enrichment solves this by enabling true ICP (Ideal Customer Profile) filtering based on firmographics, technographics, and geographic factors.
For instance, instead of relying on generic segments such as “all SaaS companies,” teams can act on enriched signals to identify who is actually worth pursuing, by narrowing their focus to SaaS companies with 100–500 employees, using Salesforce, located in North America, and showing 20%+ year-over-year growth.
This level of precision changes execution: marketing campaigns reach accounts with a higher likelihood of engagement, and the GTM team prioritizes prospects with real buying capacity.
The outcome is fewer wasted touches, better sales & marketing alignment, and higher conversion rates from a smaller, more qualified target audience.
2. Sales Velocity: Eliminating Research Time from the Buying Journey
In B2B sales, speed is a competitive advantage. Deals move faster when reps engage prospects with context—knowing the buyer’s role, tech stack, and business triggers before the first touch.
Without CRM data enrichment, reps spend 30–40% of their time researching accounts—verifying contacts, identifying decision-makers, and assembling basic context. Enriched CRM records eliminate this overhead by surfacing verified emails, direct dials, role clarity, technographics, and recent account signals directly within the workflow.
Instead of researching whether an account is relevant, reps can immediately assess ICP fit, confirm buying authority, and tailor outreach to real business events such as funding, expansion, or technology change. The result is faster engagement, fewer stalled deals, improved quota attainment, and lower Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC).
3. Intent-Driven Activation: Orchestrating GTM Timing through Behavioral Signals
Strong GTM execution depends not just on targeting the right accounts, but also on engaging them at the right time. Even well-defined ICPs underperform when teams lack visibility into buyer readiness.
CRM data enrichment enables intent-driven activation by mapping behavioral signals—content consumption, vendor comparisons, pricing page visits—directly to enriched account and contact records, allowing GTM teams to distinguish passive interest from active buying behavior and respond accordingly.
When intent signals are accurately attributed, marketing can adjust campaign sequencing, sales can prioritize outreach, and RevOps can align follow-ups across teams. This reduces ill-timed engagement, accelerates deal progression, and creates a clear advantage over competitors using static segmentation.
4. Forecast Integrity: Building Pipeline Predictability on Accurate Data
Revenue predictability depends on the quality of CRM data behind the forecast, which is a prime reason why many B2B organizations still struggle to produce reliable sales forecasts for GTM success. In Salesforce’s 2025 State of Sales study, 39% of 5,500 surveyed sales professionals report that bad data directly prevents accurate forecasting—not flawed models or lack of tools, but unreliable CRM inputs.
Consider a scenario: A $120K opportunity is forecasted to close this quarter because it’s marked as Stage 4 – Negotiation. In reality, the account hasn’t engaged in 45 days, the buyer has changed roles, and spending is on hold—none of which is reflected in the CRM. The deal stays in the committed pipeline, inflating the forecast. When this repeats across multiple deals, leadership sees a strong pipeline on paper but misses targets as deals quietly stall or slip.
CRM data enrichment fixes this by updating records with verified firmographic changes, buyer activity, and engagement signals. Deal stages are aligned to real behavior, not rep optimism. At-risk and overstated opportunities are flagged early, giving RevOps and sales leaders a realistic view of what will close, what’s at risk, and where action is needed—turning forecasting into a reliable input for GTM planning and execution.

The Role of AI in CRM Data Enrichment
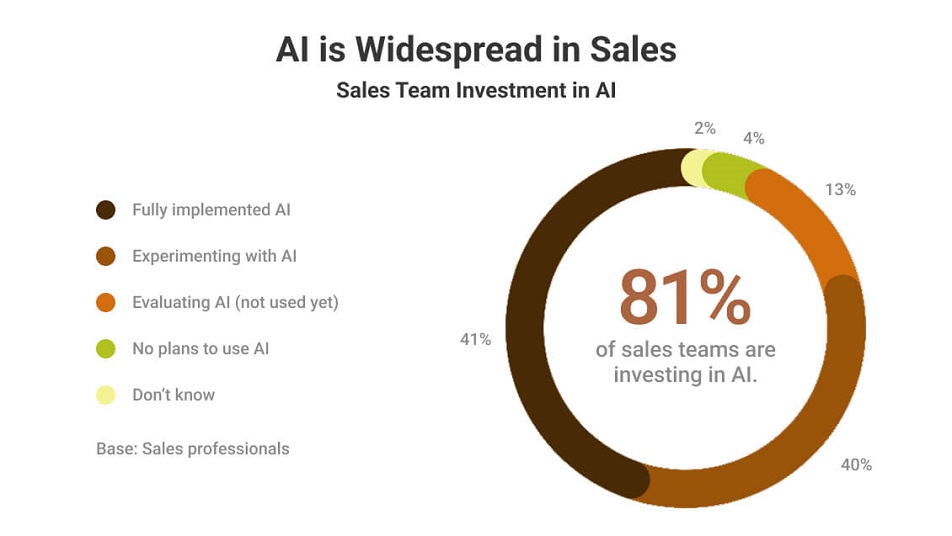
AI-powered CRM enrichment plays a critical role in GTM execution by scaling data collection, accelerating updates, and identifying patterns humans cannot process efficiently. Its value lies in ensuring that the data feeding sales, marketing, and revenue operations remains current, connected, and usable across the funnel.
Industry data supports this shift. Salesforce’s State of Sales Report 2025 shows that 83% of sales teams using AI grew revenue in the past year, compared to 66% without it—largely due to improvements in data quality, productivity, and customer personalization. These gains depend on enriched CRM foundations rendered by AI.
Here are some benefits of AI-driven business data enrichment:
Faster GTM Response through Real-Time Data Availability
AI-led CRM enrichment reduces delays between buyer activity and GTM response by continuously updating lead and account records with firmographic, technographic, and engagement-related data. Instead of waiting on manual research or batch updates, GTM teams work from CRM records that already reflect the latest account context.
This allows sales and marketing teams to respond while buyer interest is still active—shortening response times, improving handoffs, and supporting higher conversion rates without changing GTM strategy or coverage models.
Consistent Personalization in Sales and Marketing Motions
In many organizations, sales and marketing efforts fail because they operate on “data silos”—discrepant versions of the same account. AI-powered enrichment solves this by automatically refreshing CRM data and syncing it across the tech stack in real-time. AI ensures that every touchpoint—from a marketing email to a discovery call—is based on the same verified insights. With this synchronization, a prospect will not be bothered by receiving conflicting value propositions from different departments.
According to Highspot’s State of Sales Enablement 2025, the impact of this technical alignment is measurable. Organizations that successfully integrate AI-powered enrichment into their tech stacks are 42% more likely to see a significant boost in sales productivity.
When marketing campaigns and sales sequences are grounded in the same enriched data, the entire GTM engine moves in unison, reducing the “friction of misalignment” that typically slows down the buyer’s journey.
Improved GTM Prioritization through Pattern Recognition
AI-led enrichment supports GTM prioritization by analyzing patterns in enriched CRM datasets, including historical wins and losses, account attributes, and engagement signals. This helps GTM teams identify accounts that resemble their best customers and focus effort where revenue likelihood is higher.
According to IBM and Salesforce’s State of Salesforce 2024–2025, organizations classified as “Data Pioneers”—those that prioritize high-quality, enriched data—are 81% better at predicting customer expectations and 66% better at anticipating convenience needs. This advantage translates into more informed account prioritization and GTM planning.
Why Purely Automated CRM Data Enrichment Fails
AI-powered enrichment provides scale, but it operates on probability—not certainty. In GTM execution, this gap creates real risk.
Common AI-only failures include:
- Legacy Data Errors: AI often flags outdated roles because historical profiles persist, leading reps to pursue buyers who left months ago.
- Contextual Authority Blind Spots: Job titles are treated uniformly across companies, causing teams to misidentify true decision-makers.
- Technographic False Positives: Website scripts are mistaken for active tool usage, triggering irrelevant displacement strategies.
- Buying Group Fragmentation: Parent companies and subsidiaries are misclassified, creating pricing conflicts and misaligned outreach.
These issues don’t just reduce efficiency—they directly undermine deal accuracy, forecasting, and credibility in high-stakes sales motions.
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Enrichment: Closing the Accuracy Gap in AI-Driven CRM Data Enrichment
To overcome the limitations of AI-only enrichment, high-performing GTM teams adopt Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) verification. In this model, AI enriches records at scale, while human experts validate attributes that directly impact revenue decisions—buying authority, operational fit, and account structure.
This approach transforms CRM data from probabilistic updates into actionable GTM intelligence, ensuring teams act on data they can trust during real sales execution.
1. Deterministic vs. Probabilistic Intelligence
AI solutions for automated CRM data cleansing and enrichment are probabilistic; they estimate the likelihood of events, such as whether a person still holds a title. HITL is deterministic. A human can research the web and review a company’s recent “Meet the Team” blog post, cross-reference it with a press release, and confirm a promotion that occurred yesterday, weeks before an AI algorithm would pick up the “signal” by scraping data from a job board.
2. Solving the “Buying Group” Mystery
Modern B2B deals involve 6–10 stakeholders. AI can find people with the right titles, but it cannot map the internal power dynamics of a buying group. Human researchers can identify the “hidden influencers”—the Project Manager who actually owns the budget or the Technical Architect who acts as the primary gatekeeper. This is far more accurate targeting.
3. “Deep Enrichment” of Record Attributes
The best CRM data enrichment tools can often append surface data, such as company size or industry, to records. HITL data enrichment enables GTM teams to enrich their CRM with “hidden” data points, such as true budget ownership, informal buying influence, interim vs. permanent decision-makers, internal approval paths, and post-merger operating realities—that are rarely available in standard databases. Humans are better suited to uncover these signals because they can interpret ambiguity, reconcile conflicting sources, and apply contextual judgment that automated tools cannot reliably infer.

By resolving AI’s uncertainty, blind spots in buying-group dynamics, and lack of operational context, HITL enrichment transforms enriched CRM data from probabilistic updations into reliable GTM intelligence.
Scaling Human-in-the-Loop CRM Data Enrichment
Note that HITL enrichment scales effectively when implemented strategically. Not every record requires human review—only high-value accounts, active opportunities, and records where algorithmic confidence scores fall below defined thresholds. This balances accuracy requirements against operational efficiency.
Implementing Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Enrichment within Your GTM Framework
Effective implementation of a human-in-the-loop data enrichment workflow is not about validating everything—it’s about designing clear decision boundaries between automation and human judgment so speed, scale, and compliance are preserved.
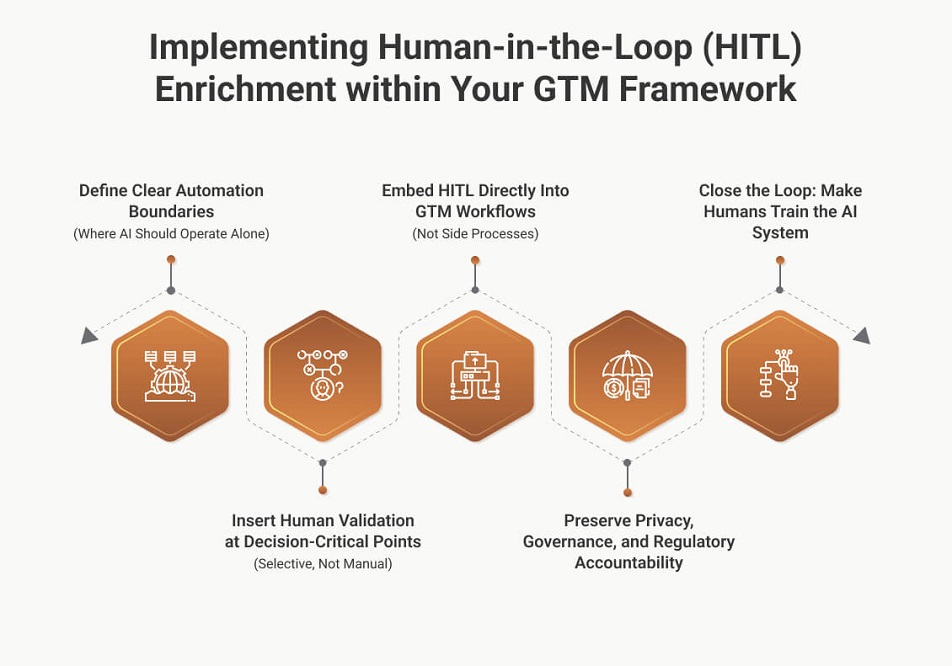
1. Define Clear Automation Boundaries (Where AI Should Operate Alone)
AI should handle high-volume, low-ambiguity tasks where rules are stable and outcomes are easily verifiable.
Keep AI fully automated for:
- Deduplication based on deterministic rules
- Field standardization (names, addresses, formats)
- Appending structured, externally verifiable attributes (industry codes, employee bands, technographics)
- Continuous refresh of fast-decaying but low-risk data (job changes, website updates)
These activities benefit from AI’s scale and speed, and errors made here are typically reversible without revenue or compliance impact.
2. Insert Human Validation at Decision-Critical Points (Selective, Not Manual)
Human-in-the-loop validation should be applied only where AI errors materially impact revenue, trust, or regulatory exposure. HITL is not a parallel enrichment process—it is an exception-handling layer for high-risk, high-impact decisions.
Where HITL is non-negotiable:
- Account structure changes: parent–subsidiary mapping, mergers, rebrands, and legal entity shifts
- Buying authority validation: distinguishing true decision-makers from interim leaders or influencer roles
- High-value or edge-case accounts: large enterprises, regulated industries, private firms, and data-poor regions
- Strategic intent signals: inputs that trigger pipeline acceleration, ABM prioritization, re-engagement, or forecast changes
How it works in practice:
- AI processes all records at scale and flags exceptions based on low confidence, conflicting signals, or high business impact
- Only a small, prioritized subset of records (typically 5–15%) is routed to human review
- Reviews are ranked by deal size, account tier, and compliance sensitivity, not volume
- SLA-governed time limits ensure human validation occurs within predictable windows, preserving GTM speed
These practices ensure GTM velocity is maintained while decision-critical records receive scrutiny.
3. Embed HITL Directly Into GTM Workflows (Not Side Processes)
HITL validation must be built into the same systems GTM teams already use—CRM, marketing automation, and sales engagement platforms—rather than added as an offline or manual step.
Effective HITL integration includes:
- CRM-native review, triggered automatically for low-confidence, high-impact, or compliance-sensitive records
- Explicit mention of validation states, to distinguish AI-enriched data from human-verified records
- Automating downstream propagation, so validated data immediately updates routing, scoring, outreach sequencing, and forecasting.
- Maintaining auditable decision logs, capturing who validated what, when, and why, for governance and regulatory defensibility
4. Preserve Privacy, Governance, and Regulatory Accountability
Both AI and humans play distinct but complementary roles in maintaining the integrity and security of sensitive data while complying with relevant privacy laws and regulations
Key safeguards:
- Humans validate interpretation and intent, not raw personal data
- AI handles ingestion and transformation; humans confirm the lawful use of data
- All AI and human interventions are documented with timestamps and rationale
- Establish clear governance rules that define which data fields can be changed by AI and which ones are off-limits
This structure aligns with GDPR, CCPA, and EU AI Act requirements without slowing execution.
5. Close the Loop: Make Humans Train the AI System
The goal of HITL is progressive improvement, not permanent manual effort.
Feedback loops include:
- Human corrections feeding back into AI confidence scoring
- Repeated error patterns triggering model recalibration
- GTM outcomes (forecast variance, win rates) informing where review thresholds shift
Over time, AI handles more volume—but humans continue to guard business meaning.

The Strategic Imperative: Using CRM Data Enrichment as Competitive Advantage
GTM strategies in 2026 face contradictory pressures:
- Buyers expect hyper-personalization, yet sales cycles must accelerate
- Targeting must be precise, yet reach must scale
- Forecasts must be accurate, yet markets remain volatile
CRM data enrichment addresses these tensions by transforming your CRM from a record-keeping system into a strategic intelligence platform. And therefore, it is no longer an operational improvement—it is a competitive requirement. As GTM teams rely more heavily on AI-driven workflows and automation, data accuracy becomes exponentially more critical.
The question for GTM leaders is not whether to enrich B2B CRM data at scale, but whether they can afford to act on probabilistic data while their competitors operate with certainty.

