
Automated invoice processing systems have significantly improved accounts payable operations by accelerating invoice approvals, reducing clerical errors, and minimizing manual staff hours. But while using automation for high-volume, rule-based validation often boosts productivity, it fails when handling non-standard or edge cases. These exceptions—ranging from mismatched purchase orders and duplicate entries to incomplete or irregular invoice formats—are where automation systems typically hit a wall.
Despite built-in artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities that enable a smart AP tool to detect and attempt to resolve anomalies, several cases involving subtle variations or context-specific errors require human judgment—something machines can’t replicate successfully yet.
If left unchecked, these lapses lead to delayed payments, approval bottlenecks, and compliance risks. That’s where human expertise comes in. Data specialists step in to validate flagged invoices, resolve edge cases, and correct data before it’s pushed into accounting or payment systems. This intervention prevents errors from cascading through financial operations, resulting in accurate records, uninterrupted workflows, and a reliable invoice-to-pay cycle.
The 100% Accuracy Myth: Current Capabilities and Limitations of Automated AP Systems
Modern Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) systems represent a form of Business Process Automation (BPA) that has significantly improved invoice processing by managing high-volume, repetitive tasks. These systems can extract data with up to 90% accuracy from:
- Structured Invoices from regular vendors
- Standard invoice formats with consistent layouts
- Large volumes of invoices with predictable data fields
Such automation reduces manual workload, speeds up processing times, and minimizes routine errors in highly standardized environments. Yet, real-world invoice data processing often involves far more variability than automation alone can handle.
The 10% Problem: Common Edge Cases Automation Misses
Even with such high-end systems, subtle invoice data processing challenges persist, like:
Invoice Scanning Errors and OCR Reading Issues
- Handwritten notes or signatures that look like scribbles
- Poor quality scans (like trying to process a faded receipt)
- Unusual fonts or damaged documents
Data Mismatch Problems
- Vendor names appearing differently (“ABC Corp” vs. “ABC Corporation”)
- Currency conversion errors
- Invoice dates that seem unreasonable (like a date from 1995 on a current invoice)
Complex Invoice Formats
- Multi-page invoices with detailed breakdowns
- Mixed currencies on international orders
- Invoices with multiple tax rates per line item
Duplicate Invoice Detection Struggles
- Similar invoices arriving within minutes of each other
- Partial duplicates where amounts differ slightly
Non-PO Invoice Handling Complications
- Unstructured expense receipts (like a handwritten taxi receipt)
- Invoices without established profiles
- Misc. charges that don’t fit standard categories
These challenges demonstrate that while automation handles the predictable, a significant number of unpredictable exceptions will always remain.
The Real-World Impact of “Almost Accurate Data”
While advanced systems typically achieve 90% accurate data via straight-through processing for standard invoices, the remaining 10% creates exceptions that can create significant business challenges, like:
- Delays in payment processing, leading to strained vendor relationships
- Cash flow disruption when invoices get stuck in exception handling queues
- Increased processing costs from manual intervention for invoice exception handling
- Compliance and audit risks arising from mismatched or incomplete documentation
Dealing with Frequent Invoice Errors?
Learn how top finance teams reduce exceptions by combining automation with expert human validation.
Can Automation Fix Its Own Mistakes?
It is critical to identify the boundaries of error recognition and self-learning in these intelligent invoice data processing systems.
While automation can’t always recognize its blind spots, today’s automated invoice processing tools are far from static. Many include built-in mechanisms that help identify issues early, adapt based on past corrections, and validate outputs even after processing. These capabilities don’t eliminate errors, but they do enable automation to catch, learn from, and correct a significant portion of them before they impact downstream workflows.
Self-Correction Mechanisms that Automated AP Tools Typically Have
1. Real-Time Error Detection
This is the first line of defense, catching problems as soon as they appear.
- Exception Reporting: Think of this as an automated quality controller. If an invoice shows a suspicious charge, like a $10,000 bill for office supplies when the average is $500, the system immediately raises a red flag for review.
- Rule-Based Validation: This approach requires using pre-defined, logical rules to set data checks and flags invoices that violate these non-negotiable checks, like:
- An invoice date that is in the future
- A total amount field that is left empty
- Numerical values that exceed a set limit
- Machine Learning: Every time a data expert corrects an error, the system remembers it. This is similar to a smart autocorrect feature getting better as it is used. The system learns from each example, helping it handle similar invoices correctly in the future.
- Pattern Recognition: The system analyzes thousands of invoices to spot patterns that consistently report exceptions. Like, if it repeatedly struggles with invoices from a specific vendor, it automatically adjusts its approach to that vendor’s format.
- Invoice Reconciliation: The system compares processed invoices with purchase orders and delivery receipts to ensure everything matches up.
- Periodic Audits: The system runs automated reviews regularly to identify issues that may have slipped through the initial checks.
- Data Analytics: The system tracks and reports on error patterns. For example, it might discover that 80% of errors are tied to a specific invoice format, thus allowing for a targeted fix.
- A vendor sends a dual-currency invoice with no prior precedent
- An invoice appears valid but contains a fraudulent line item formatted to bypass rules
- A PO number uses an unusual naming convention that misguides the match
- High Priority: Reserved for issues with significant financial implications, such as large invoice amounts, urgent payment deadlines, or critical vendors.
- Medium Priority: For standard business rule violations that are not immediately critical but require attention.
- Low Priority: For minor issues like formatting errors or slightly blurry data that don’t impede processing.
- Routing extraction errors to Data validation specialists
- Routing approval requirements to Finance teams
- Routing exceptions related to purchase order mismatches to the Procurement teams
- Manual Exception Handling: Experts verify and validate bottlenecks that automated systems cannot resolve, such as deciphering unclear data, validating information against source documents or purchase orders, securing missing approvals, and ensuring data consistency.
- Quality Assurance: They perform final accuracy checks on high-value or complex invoices, matching amounts, verifying vendor information, and validating all dates.
- Complex Vendor Disputes: Issues that involve historical context or ongoing negotiations
- Highly Ambiguous Data: Invoices with vague descriptions, unclear line items, or non-standard documentation
- Non-Standard and Unfamiliar Formats: Failing to process invoices from new or small vendors, deviating from established templates
- Suspicion of Fraud: Subtle inconsistencies that hint at fraudulent activity that don’t always trigger a standard exception rule
2. Learning and Improving over Time
The system gets smarter with every correction it makes. The process, often called machine learning in invoice processing, is key.
3. Catching Errors after Processing
Even after an invoice is processed, the system can do multiple layers of final checks, like:
But What Happens when Automation Hits a Wall?
Through machine learning and pattern recognition, automated invoice processing systems improve over time, especially when human users consistently correct the same types of errors. For instance, if a system regularly sees tax fields misaligned from a specific vendor, it can eventually adjust its handling of that format.
But this kind of learning is reactive, slow, and heavily pattern-dependent. What happens when the error is new, subtle, or context-specific?
These aren’t standard errors – they’re edge cases. And automation doesn’t question them. It doesn’t ask, “Is this unusual?” It just processes and moves on.
This is the critical limitation: AI can only correct what it can recognize, and it often fails to identify when it’s wrong, leading to hallucinations.
That’s where exception handling (automated and manual) comes into play. When systems encounter data they weren’t trained on or anomalies that fall outside established patterns, human oversight plays a critical role in validating and correcting those outliers. The result is a continuously improving system that performs with greater precision over time.
The Hybrid Invoice Processing Model: The Path to 100% Accuracy
Collaboration Between Invoice Automation And Data Experts
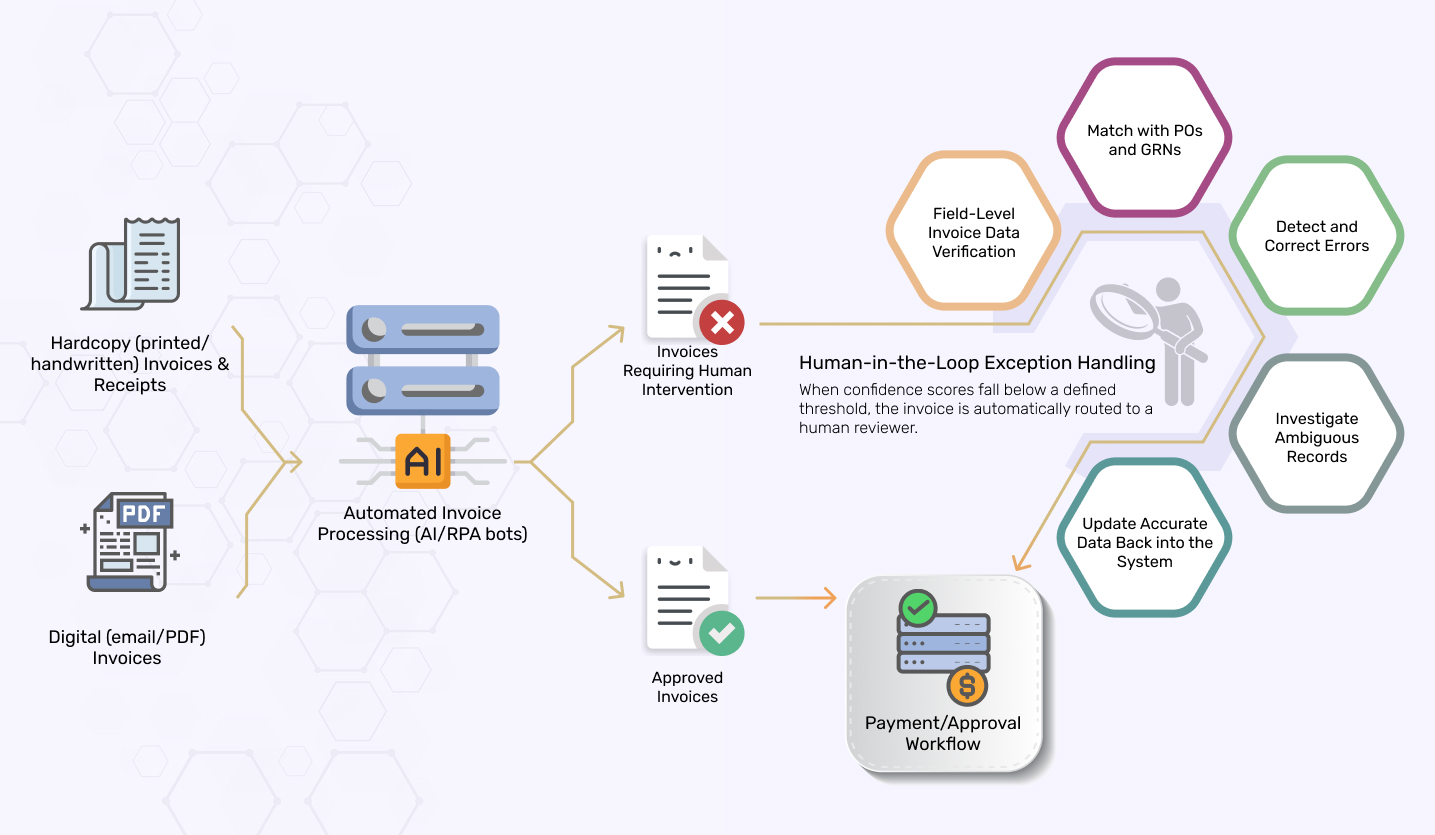
When an invoice requires special attention, a human-in-the-loop invoice processing and exception management workflow gets activated. This hybrid invoice processing combines automated identification with the precision of a human expert to ensure every issue is handled effectively, creating a reliable AP workflow management system.
Initial Processing and Detection
Step 1: Invoice Intake Process
Invoices enter the system in various formats and from multiple channels, including scanned images, emailed PDFs, and online portals.
Step 2: OCR and Data Extraction
The system uses Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology to read and extract key invoice details such as the vendor name, invoice number, date, line items, amounts, and tax information.
Step 3: Primary Validation
The system conducts an initial check, verifying fields and consistency. This also triggers the approval workflow for specific invoices.
Step 4: Exception Identification and Funneling
If any primary checks fail, the system flags the invoice as an exception and funnels it into a dedicated exception management workflow for detailed invoice validation.
Human-in-the-Loop Exception Management Workflow
Step 5: Categorization & Prioritization
The system triages exceptions based on their severity and impact.
Example:
A $50,000 invoice with a missing purchase order is flagged for immediate attention, while a $25 receipt with a slightly blurry date can be addressed later.
Step 6: Smart Routing
Then, the system uses its knowledge of the exception type to route it to the appropriate team or individual, like:
Step 7: Exception Resolution and Final Processing
This is the final stage where the exception is closed. The designated subject matter expert or domain professional takes the necessary action to fix the flagged issue. Once the issue is resolved, the corrected invoice is automatically pushed back into the main processing workflow for a final system validation. If it passes, it proceeds to payment and is integrated into the company’s financial systems, closing the loop on the exception.
This involves-
Step 8: Resolution Tracking & Audit Trails
The automated AP tool tracks every exception, providing a detailed audit trail for accountability and a clear record of every action taken. This ensures high invoice quality assurance.
The Limits of AI in Exception Handling
Even with sophisticated self-correction mechanisms, certain exceptions continue to pose a challenge to automated systems. These issues require a level of critical thinking that an algorithm simply cannot provide.
Persistent Challenges Beyond the Scope of AI:
This is where a hybrid invoice exception handling approach becomes the final, crucial step in completing the technology-driven process and ensuring accurate outcomes.
The Benefits of Human Intervention in Automated Invoice Processing
By incorporating human expertise into the automation workflow, businesses can achieve significant operational and strategic benefits. This is a crucial component of an accurate invoice data processing solution.
Optimized Operational Costs
Reduces manual processing and error correction, lowering costs and freeing up staff for strategic work.
Strengthened Supplier Relationships
Timely and accurate payments, ensured by human validation, build trust and improve supplier relationships.
Enhanced Financial Visibility
Accurate data provides a reliable foundation for financial reporting and forecasting, leading to better-informed business decisions.
Improved Staff Productivity
Frees up staff from tedious error resolution, allowing them to focus on value-added activities and increasing overall productivity.
Ready to Transform Your Accounts Payable Error Resolution Process?
Connect with specialists who understand the nuances of automated invoice processing solutions and can help you achieve optimal accuracy rates through manual data validation.
Conclusion
While automated systems achieve impressive accuracy, reaching 100% invoice processing accuracy requires strategic human oversight and exception handling. The most successful organizations combine advanced automation with specialized data validation expertise, knowing that different challenges need different solutions.
The future of invoice processing isn’t about choosing between technology and human expertise – it’s about optimizing how they work together. Organizations that invest in this hybrid approach consistently achieve the highest accuracy rates and most efficient workflows, turning invoice processing from an operational challenge into a competitive advantage.

