
APIs have become the backbone of digital transformation.
→ In 2023, API traffic accounted for nearly 60–71% of overall web traffic, according to Cloudflare and Imperva reports.
→ At the same time, Postman’s 2024 State of the API survey highlighted that 74% of organizations now identify as API-first, a sharp rise from just a few years ago.
However, as a single enterprise application now connects to between 26 and 50 API endpoints, manual configurations, spreadsheets, and ticket-driven API ops are no longer sufficient. In fact, even early forms of API management automation, using tools like Swagger or custom scripted deployments, are insufficient as machine-to-machine interactions increase.
This scale has redefined how businesses think about API management, governance, and operations. What’s needed is a shift from manual to autonomous API management, guided by APIOps and closed-loop governance. With API lifecycle automation, platforms not only deploy and monitor APIs but also detect risks, enforce policies, and self-remediate in real time. Let’s explore this shift from manual to autonomous API management in greater detail.
Table of Contents
- The Shift in API Development & Integration
- Exploring the API Shift: Manual → Automated → Autonomous
- How Autonomous API Management Works?
- What ‘Autonomous’ API Management Looks Like in Action?
- Transformation Playbook: Strategic Implementation Roadmap
- Navigating the API Transition
- Security and Ethical Considerations in Autonomous API Management
- Concluding Note
The Shift in API Development & Integration
In the early days, APIs were designed primarily for human-centric interactions, serving as channels for developers or applications to send queries and retrieve responses from systems. Governance and deployment followed this model with manual approvals, developer reviews, and perimeter security.
This paradigm has changed today. APIs now support machine-to-machine (M2M) interactions, from cloud workloads and IoT devices to AI Agents calling other services in real-time. This evolution requires decisions at runtime velocity, where human oversight alone cannot keep up.
Consequently, organizations are shifting toward APIOps and intelligent API lifecycle automation, setting the stage for autonomous management.
Exploring the API Shift: Manual → Automated → Autonomous
The journey of API management reflects how organizations have matured their digital operations. It began with manual oversight, evolved into automation, and is now advancing toward autonomy. Each stage in the process of shifting from manual to autonomous API management presents distinct practices, limitations, and outcomes.
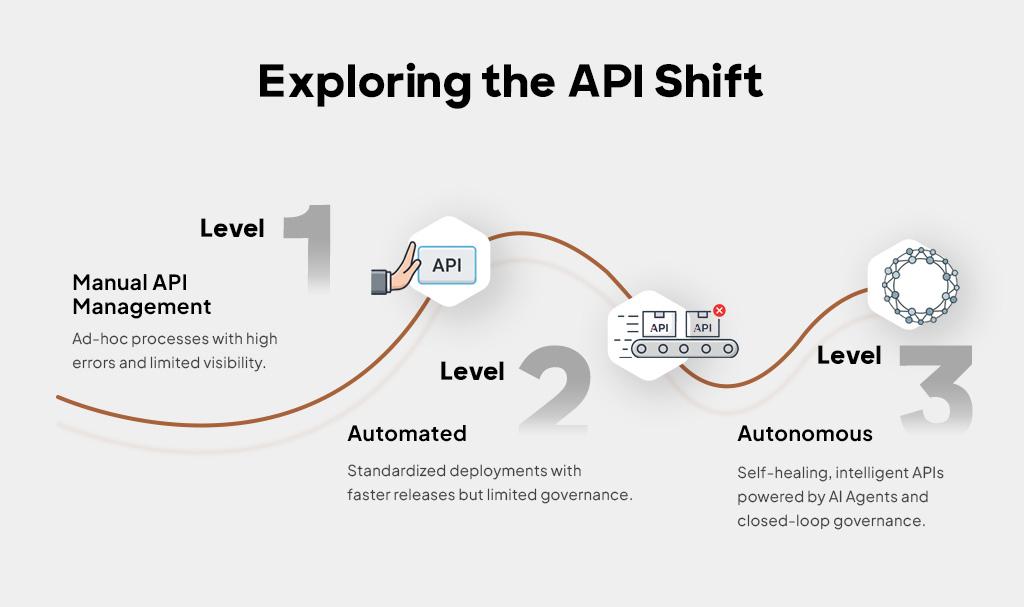
Level 1 – Manual
Characteristics: APIs are deployed and managed through ad-hoc processes. Inventories are tracked in spreadsheets, keys are provisioned manually, and approvals move through ticket-based workflows. Security relies heavily on perimeter defenses and after-the-fact monitoring.
Pain Points:
- High error rates
- Limited visibility
- Slow release cycles
Impact:
- Increased risk from shadow APIs and compliance failures
- Delayed product launches
Level 2 – Automated
Characteristics: API automation leveraged repeatability and brought consistency into the API development & integration process. Organizations used tools like Postman and Swagger to integrate APIs into CI/CD pipelines, enforce policy templates, and run contract testing. This stage improved efficiency but still required human intervention to remediate incidents or enforce compliance.
Pain Point:
- Automation covers deployment but lacks real-time governance and self-healing.
Impact:
- Faster releases and better consistency, but persistent risks from policy drift and shadow APIs.
Level 3 – Autonomous
Characteristics: Autonomous API management builds on automation by adding closed-loop governance. AI Agents are used to continuously discover new endpoints, apply baseline policies, monitor runtime traffic with ML-driven analytics, and execute automated remediation. This is where typical APIOps best practices evolve into self-healing workflows, addressing risks and optimizing performance without human approval.
Pain Point:
- Complexity of scaling governance across thousands of intelligent APIs in dynamic, multi-cloud environments.
Impact:
- Real-time resilience, reduced MTTR (Mean Time To Repair), higher compliance coverage, and improved cost control.
You can read more about intelligent APIs and autonomous API management here: Autonomous APIs – When AI Agents Call the Shots.
How Autonomous API Management Works?
It may appear so, but autonomous API management is not just an extension of automation. It introduces closed-loop governance that allows systems to adapt, remediate, and optimize without waiting for manual intervention. This enhancement is tied to the rise of AI Agents and intelligent APIs. Unlike traditional users, AI Agents operate autonomously, chaining multiple APIs together and approving/denying access in real-time.
Architectural Components
- Control Plane
Central catalog for all APIs (REST and event-driven). Registers new or shadow endpoints, enforces lifecycle states, and maps ownership.
- Data Plane
API gateways and service mesh sidecars that apply routing, security, and traffic control. Ensures consistent API management automation across environments.
- Observability & APIOps
Telemetry from logs, traces, and metrics feeds for anomaly detection. Integrated with APIOps tools, it enables API lifecycle automation and runtime feedback loops.
- Policy Engine
Policy-as-code for authorization, authentication, and compliance. Frameworks like OPA ensure consistency and drift-free enforcement through GitOps pipelines.
- Agentic Governance
Extends governance to AI agents and other non-human consumers. Manages identities, quotas, and usage limits to prevent overconsumption and compliance risks.
Operational Components (People & Processes)
Technology alone does not deliver autonomous API management. It requires clear ownership and disciplined processes to align with APIOps best practices.
Key Roles
- API Product Owners – Define business priorities, manage the API portfolio, and align APIs with product strategy.
- Platform Engineers – Build and maintain the control and data planes, ensuring smooth deployment and scalability.
- Security Engineering (API Red Team) – Continuously test APIs for vulnerabilities, enforce compliance, and simulate attacks to validate defenses.
- FinOps Teams – Monitor API and LLM usage costs, set consumption thresholds, and optimize spend across agentic workloads.
Core Processes
- Policy-as-Code Reviews – Policies are versioned and reviewed through pull requests before deployment.
- Runtime Guardrails – Automated rules block unsafe changes or policy drift in production environments.
- Shadow API Audits – Continuous discovery of unmanaged endpoints, with automated remediation workflows.
- Cost and Quota Controls – Usage tracking tied to budgets, ensuring AI agents and services stay within approved limits.
- Closed-Loop Feedback – Incident learnings and runtime telemetry feed back into design and deployment workflows, enabling step-by-step API lifecycle automation.
What ‘Autonomous’ API Management Looks Like in Action?
| Continuous Discovery & Classification | Policy Alignment & Enforcement | Monitoring & Anomaly Detection | Remediation & Optimization | Feedback & Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The first step is to identify and categorize all APIs within your ecosystem continuously. | Once APIs are classified, policies are applied to ensure they meet governance, security, and performance standards. | This stage involves observing API performance and usage in real-time. Advanced analytics detect deviations from normal operation. | Upon detecting anomalies, AI Agents trigger automated actions (from blocking malicious requests to scaling resources) to resolve issues | The final stage closes the loop by feeding insights from monitoring and remediation back into the system, ensuring the workflow constantly adapts. |
Transformation Playbook: Strategic Implementation Roadmap
Transitioning to autonomous API management is not a single-step transformation. The transition often spans several months to multiple years, depending on the scale of APIs, legacy reliance, and organizational readiness.
Month 01-02: API Discovery & Baseline
- Continuous discovery & classification of all APIs, including shadow and unmanaged endpoints.
- Normalize API documentation and versioning using tools like OpenAPI 3.1 and AsyncAPI 3.0 for consistency.
- Establish a baseline catalog with ownership, sensitivity, and business criticality tags.
- Define executive KPIs (e.g., % managed APIs, policy compliance rate, shadow API reduction targets).
Month 03-06: Automate API Controls
- Implement API lifecycle automation through CI/CD pipelines, contract testing, and linting.
- Deploy policy-as-code frameworks (e.g., OPA/Rego) and integrate with GitOps workflows.
- Introduce developer portals for onboarding and self-service access management.
- Begin runtime monitoring with APIOps tools to detect anomalies and enforce policy consistency.
Month 07-12 or More: Intelligence Phase
- Enable real-time anomaly detection using ML-driven observability pipelines.
- Establish agentic governance to manage AI Agent traffic, identities, and quotas.
- Deploy automated remediation workflows that can throttle, revoke, or isolate endpoints without human intervention.
- Expand monitoring into FinOps to track API and LLM usage costs, enforcing quota and budget controls.
- Close the loop with feedback-driven continuous improvement, ensuring step-by-step API lifecycle automation evolves into full autonomy.
Navigating the API Transition
Unifying APIOps, lifecycle automation, and policy-as-code is inherently a complex thing to achieve. You may face the following API automation challenges:
→ Difficulty in discovering and cataloging shadow APIs (undocumented/unapproved APIs) across distributed systems
→ Lack of alignment between manual vs automated API deployment processes, leading to policy drift
→ Inconsistent security enforcement across hybrid and multi-cloud environments
→ Limited skills and resources to adopt and scale APIOps tools effectively
→ Rising costs of API and LLM traffic without transparent FinOps governance
Overcoming the Challenges with Professional API Services
Our API services are designed to help organizations accelerate this shift. From automated API deployment to building custom AI Agents for autonomous API management, we provide:
- End-to-end API design, deployment, optimization, and orchestration
- Step-by-step API lifecycle automation aligned with business priorities
- Security-first governance, covering shadow APIs, compliance, and agentic traffic
- Cost management strategies for APIs and AI Agent workloads
Learn more here: API Development & Integration Services
Security and Ethical Considerations in Autonomous API Management
The shift to automated or autonomous API management has also amplified risk, primarily because of inefficiencies in validating or securing APIs.
This is reminded by incidents like:
- Dell’s API breach (May 2024) that exposed 49 million customer records via an API in the partner portal, revealing shortcomings in autonomous throttling and anomaly detection.
- T-Mobile’s API breach (2023), where a misconfigured API leaked personal data of over 40 million users.
- Optus API breach (2022), where unauthenticated API endpoints exposed ID numbers and addresses, affecting more than 10 million accounts.
- On the AI front, a critical failure occurred when a private xAI API key was accidentally leaked via GitHub, exposing access to 52 large language models.
These breaches aren’t just technical failures; they had real consequences, from legal exposure to reputational damage and financial loss.
Concluding Note
The progression from manual oversight to autonomous API operations has reshaped how enterprises run their digital ecosystems. With modern API lifecycle workflows, organizations can now manage APIs with greater speed, consistency, and scale without significant human intervention.
Yet, security remains an unresolved challenge. Cloudflare notes that despite ~60% of internet traffic being driven by APIs, up to a quarter of endpoints still remain unknown or unmanaged. This has resulted in a sharp increase in API-related breaches and attacks, reinforcing the urgency of stricter management.
Autonomous API systems address much of this by discovering hidden endpoints, monitoring behavior, and remediating risks in real-time. However, not every decision can be automated. Issues such as regulatory interpretation, ethical considerations, or business trade-offs require human judgment. Compliance validation and accountability depend on context that machines cannot fully grasp, which is why strategic oversight remains indispensable.
The most resilient enterprises will combine self-governing APIOps with expert-driven leadership, ensuring APIs remain secure, reliable, and business-aligned.
At SunTec, we support organizations in such transitions with expert-driven leadership and by laying the groundwork for truly autonomous operations. Get in touch with our API and automation experts whenever you’re ready.

